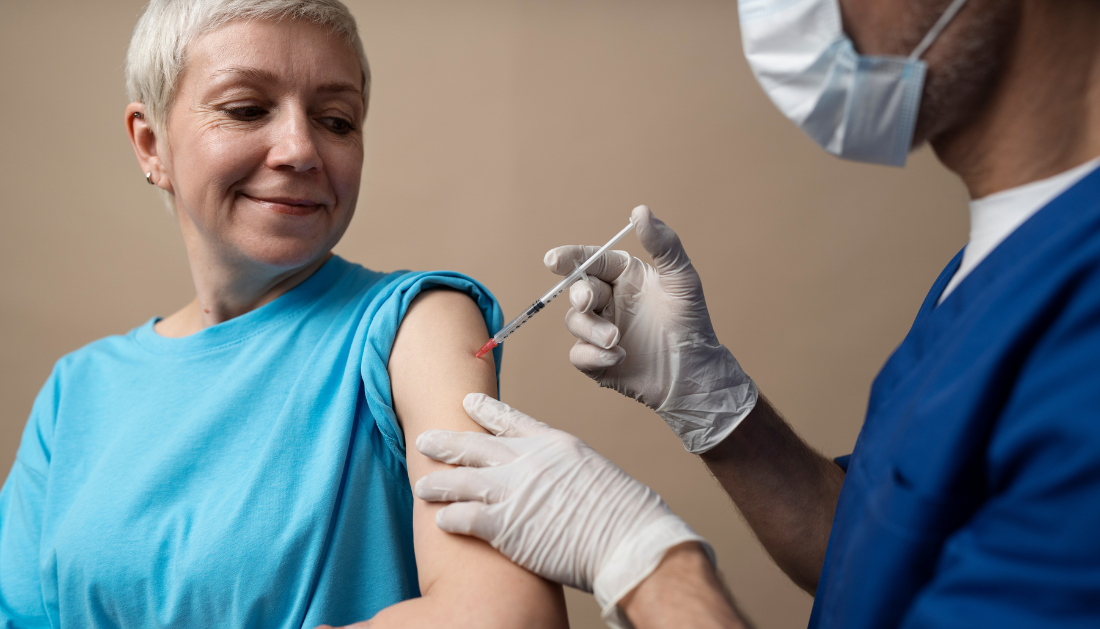

Using shared clinical decision-making, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) advised on June 21, 2023, that persons 60 years of age and older may receive a single dose of Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccines. The ACIP decided on June 26, 2024, to update these guidelines, which now state that a single dose of the RSV vaccine should be administered to all adults ≥75 years of age and individuals 60–74 years of age who are at elevated risk for severe respiratory syncytial virus
The goal of these revised recommendations is to increase the number of people who are most likely to benefit from RSV vaccine. Sustained post-licensure surveillance will direct subsequent suggestions.
In the United States, throughout the fall and winter, respiratory syncytial virus is a leading cause of hospitalizations and respiratory illnesses in older persons. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) of the CDC released its first recommendation for adult RSV vaccination on June 21, 2023. The recommendation said that individuals who are 60 years of age or older may receive a single dose of the vaccine through shared clinical decision-making.
In the spring of 2024, it was predicted that 20% to 25% of American individuals over 60 had received the RSV vaccine. Additionally, the first postlicensure safety and effectiveness data for GSK’s Arexvy and Pfizer’s Abrysvo were made available. Furthermore, on May 31, 2024, the FDA authorized mResvia [Moderna], the third respiratory syncytial virusvaccine, to prevent its associated lower respiratory tract disease (RSV-LRTD) in people 60 years of age or older.
The ACIP reviewed fresh data from randomized, observer-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (RCTs) of mResvia, postlicensure data on Arexvy and Abrysvo, and data from prior meetings in order to update recommendations for adult RSV vaccine. The evidence is compiled in this study, which also offers the most recent ACIP guidelines for RSV vaccination in individuals 60 years of age and older.
Future Adult RSV Vaccination Policy
The FDA approved the use of GSK’s Arexvy on June 7, 2024, for people who are 50–59 years old and at risk of RSV-LRTD. In June 2024, the ACIP determined that there was not enough data to make a decision about respiratory syncytial virus vaccination strategy for individuals 50–59 years old who are more likely to contract the disease.
The following things are required, according to ACIP, before voting on a recommendation for this age group: updated RSV vaccine safety analyses for adults over 60 years of age, which include data on immunogenicity in adults with immunocompromise, additional information on the length of protection from this vaccination and immune response following revaccination, and results from the entire 2023–2024 RSV season in the FDA analysis incorporating chart confirmation of GBS diagnoses. When more information becomes available, ACIP will evaluate the evidence and cast a vote on the RSV immunization policy for this age range.
more recommended stories
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?
Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?Key Takeaways High-dose antioxidant supplementation in.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.
 Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New Study
Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New StudyKey Summary Cross-sectional analysis of 8,320.
 Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood Metabolites
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood MetabolitesKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) Researchers identified.
 Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge Drinking
Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge DrinkingKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Durvalumab in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Survival vs Cost
Durvalumab in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Survival vs CostKey Points at a Glance Durvalumab.
 Rising Chagas Parasite Detected in Borderland Kissing Bugs
Rising Chagas Parasite Detected in Borderland Kissing BugsKey Takeaways (At a Glance) Infection.
 Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis Insights
Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis InsightsKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) A Clinical.

Leave a Comment