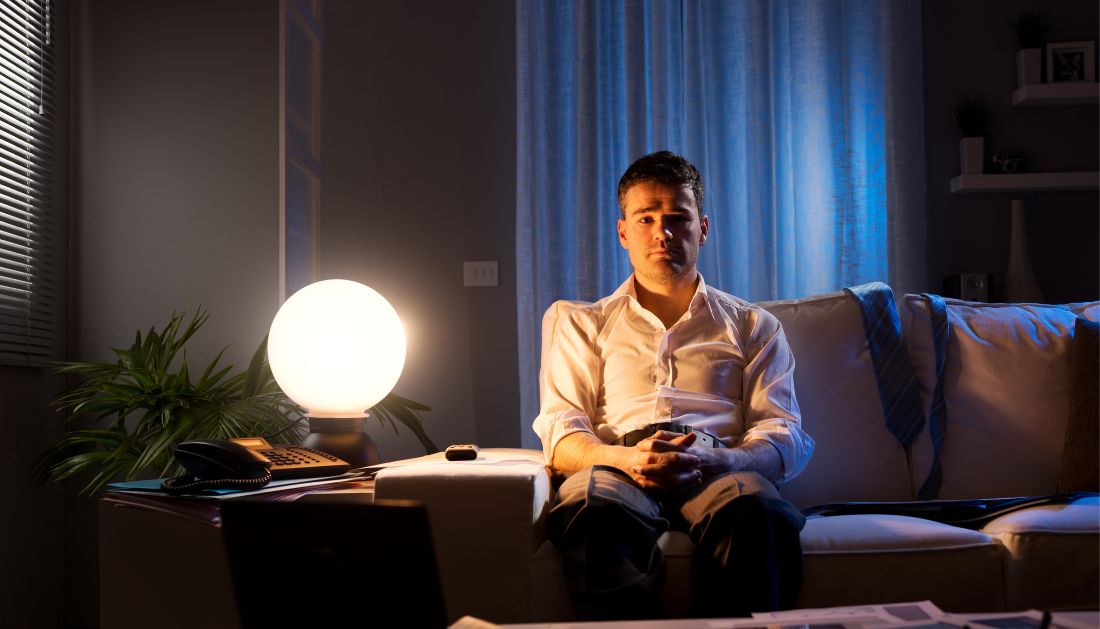


The Power of Perception: How Society Shapes Loneliness
A groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications reveals that our perception of being alone plays a crucial role in determining whether solitude feels peaceful or lonely. Researchers found that negative portrayals of being alone—especially in media and public health campaigns—reinforce loneliness, while a positive mindset can reduce it.
With global loneliness levels reaching epidemic proportions, experts suggest that reframing alone time as beneficial rather than harmful could be a cost-effective way to improve mental health.
How Media and Public Health Messaging Shape Loneliness
- Analysis of 144 U.S. news articles (2020-2022) found that media is 10 times more likely to frame solitude negatively rather than positively.
- Headlines were twice as likely to emphasize the dangers of being alone rather than presenting neutral information.
- Alarmist messaging in public health campaigns may unintentionally increase loneliness by fostering fear around solitude.
The Science Behind Solitude and Mental Health
The study conducted controlled experiments and experience-sampling research across nine countries to explore how individual beliefs about solitude impact loneliness risk.
Key Findings:
- Those who view being alone negatively experienced a 53% increase in loneliness after spending time alone.
- Those with positive beliefs about solitude reported a 13% decrease in loneliness after the same experience.
- Cross-cultural comparisons showed that Japanese individuals—who generally see solitude as restorative—report lower loneliness rates than Westerners.
- Countries with higher loneliness rates tend to have more negative societal attitudes toward solitude.
“For people who already feel lonely, changing how they think about alone time could be a powerful mental health intervention.”
Rethinking Alone Time: A New Approach to Reducing Loneliness
The study suggests that instead of warning against loneliness, public health campaigns should also highlight the benefits of solitude, such as:
- Personal growth & self-reflection
- Enhanced creativity & problem-solving
- Improved emotional regulation
“Fostering positive beliefs about alone time may offer a cost-effective, scalable way to reduce loneliness—particularly for those at greatest risk.”
Conclusion: Can Mindset Be a Key to Fighting Loneliness?
As loneliness becomes a global health crisis, this study challenges the negative stigma around solitude and suggests that changing how we think about being alone may be just as important as social connection in combating loneliness.
More Information: Rodriguez, M., Schertz, K.E. & Kross, E. How people think about being alone shapes their experience of loneliness. Nat Commun 16, 1594 (2025), DOI – 10.1038/s41467-025-56764-3, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-56764-3
more recommended stories
 Stem Cell Therapies Course for Parkinson’s Disease Clinicians
Stem Cell Therapies Course for Parkinson’s Disease CliniciansKey Summary The International Society for.
 Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety Concerns
Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety ConcernsKey Summary Experts publishing in The.
 Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent Allergies
Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent AllergiesKey Summary Researchers at Stanford University.
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US States
Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US StatesKey Points Researchers developed a new.
 Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic Type
Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic TypeKey Summary A new study from.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights Benefits
Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights BenefitsKey Points at a Glance A.
 Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat Diet
Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat DietKey Points A high-fat diet accelerated.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.

Leave a Comment