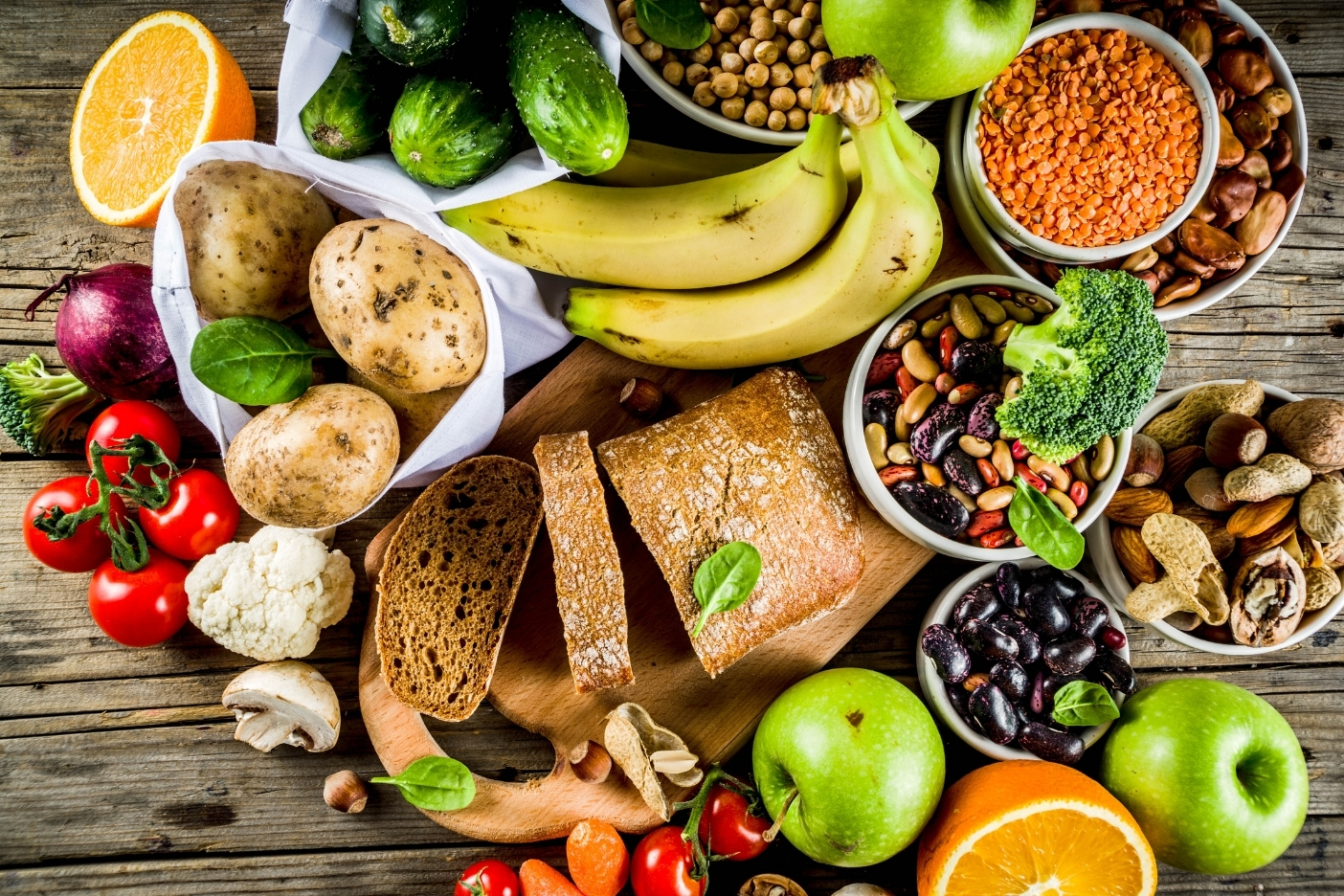


A meta-analysis of 29 controlled-feeding studies sheds new light on the relation between macronutrient composition and total energy expenditure, according to a recent study published in The Journal of Nutrition.
The concept of energy balance and body weight regulation states that when energy intake is greater than energy expenditure excess calories are stored in the body with a subsequent increase in body weight. In this view, diets of equal caloric value but having differing ranges of macronutrient composition from very-low-carbohydrate to very-low fat should yield similar physiological impact. However, how the body uses calories is not that simple according to lead author David Ludwig (Harvard Medical School) and coauthors, which may account for divergent findings among studies.
The effect of macronutrient composition on total energy expenditure remains controversial, according to the study authors. “One possible explanation for this inconsistency may be study duration as a physiological adaptation to lower carbohydrate intake may require 2 to 3 weeks.”
To test the hypothesis that the effects of carbohydrates, expressed as a percent of energy intake on total energy expenditure vary with time, study results from a previous meta-analysis and those identified in new trials were analyzed. The duration of the studies, which included 617 participants, ranged from 1 to 140 days, with the difference in carbohydrate intake from 8% to 77%.
Among the 23 shorter trials (< 2.5 weeks), total energy expenditure was slightly reduced on lower-carbohydrate diets. In contrast, the longer duration lower-carbohydrate diet substantially increased total energy expenditure. It was estimated that these diets increased energy expenditure by ∼50 kcal per day for every 10% decrease in carbohydrates (expressed as % energy intake).
Research conducted by ASN members and other scientists can provide critical information important for policy development. This webinar will help ASN members understand the nature of nutrition science policy and how it interfaces with nutrition research as well as the way in which research is integrated into policy development.
The authors conclude that contradictory findings of diets with different macronutrient compositions on total energy expenditure appear to arise, in part, from differences in study duration. These results highlight the importance of longer trials to understand chronic macronutrient effects and to better understand mechanisms whereby lower-carbohydrate diets may facilitate weight loss.
A corresponding editorial provides further perspective regarding the optimal diet composition for body-weight control. Researchers Faidon Magkos and Arne Astrup (University of Copenhagen) stress the importance of experimental testing in humans to better understand the metabolic nuances and interrelations between diet composition, metabolic fuel availability, body composition, and energy expenditure at various stages of the natural course of obesity.
more recommended stories
 Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent Allergies
Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent AllergiesKey Summary Researchers at Stanford University.
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights Benefits
Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights BenefitsKey Points at a Glance A.
 Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat Diet
Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat DietKey Points A high-fat diet accelerated.
 Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA Analysis
Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA AnalysisKey Takeaways Serial liquid biopsies using.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain Changes
Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain ChangesKey Takeaways Brain vascular health is.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.

Leave a Comment