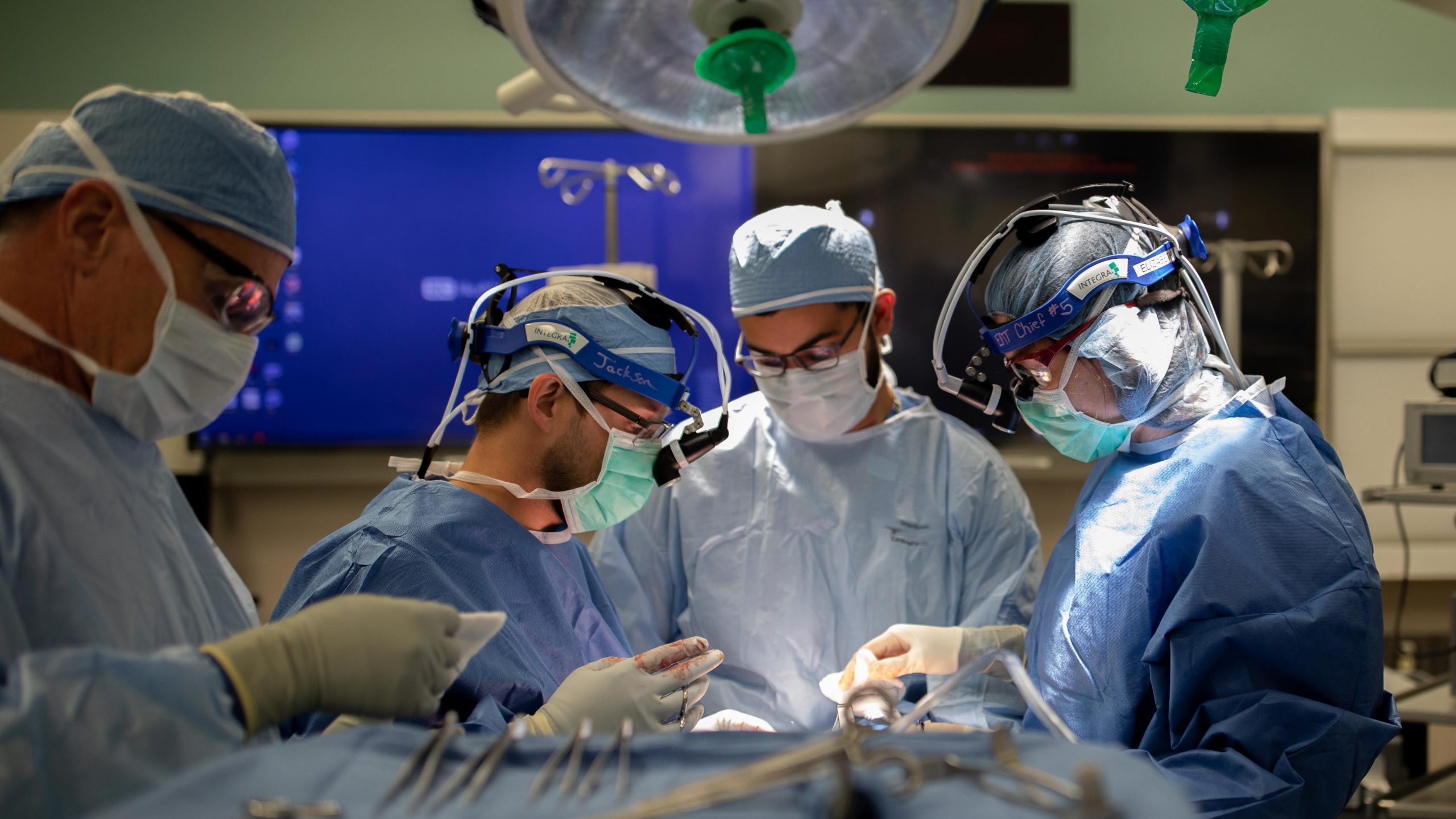

Jose Zevallos, MD, division chief of Head and Neck Surgery in the Department of Otolaryngology at Washington University has developed a new niche in his head and neck practice – endocrine surgery. He is now among the busiest thyroid and parathyroid surgeons in the region, doing several cases each week between Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Christian Hospital Northeast. He finds the surgery both rewarding and challenging.
“While these surgeries are commonly done, improved outcomes are associated with high-volume surgeons,” he said. “A significant part of my practice focuses on second opinions, advanced cancers, and repeat surgeries in patients who previously had incomplete resections or develop thyroid cancer recurrence.”
Many patients who get thyroid and parathyroid surgery are otherwise very healthy and tend to be young. Quality of life and excellent surgical outcomes are very important. The nerves that move the vocal cords and help give your voice pitch and tone need to be identified and kept safe during surgery. Zevallos agreed this is probably his most important concern as the surgeon.
Surgery involves the removal of all or part of the thyroid gland or one or more parathyroid glands. These procedures can impact hormones produced by these glands for distribution throughout the body.
“Working closely with endocrinology in deciding candidacy for surgery is another very rewarding part of my role,” said Dr. Zevallos. “Not every patient with a thyroid nodule needs a biopsy or surgery, and making multidisciplinary decisions along the way ensures the best outcomes for our patients.”
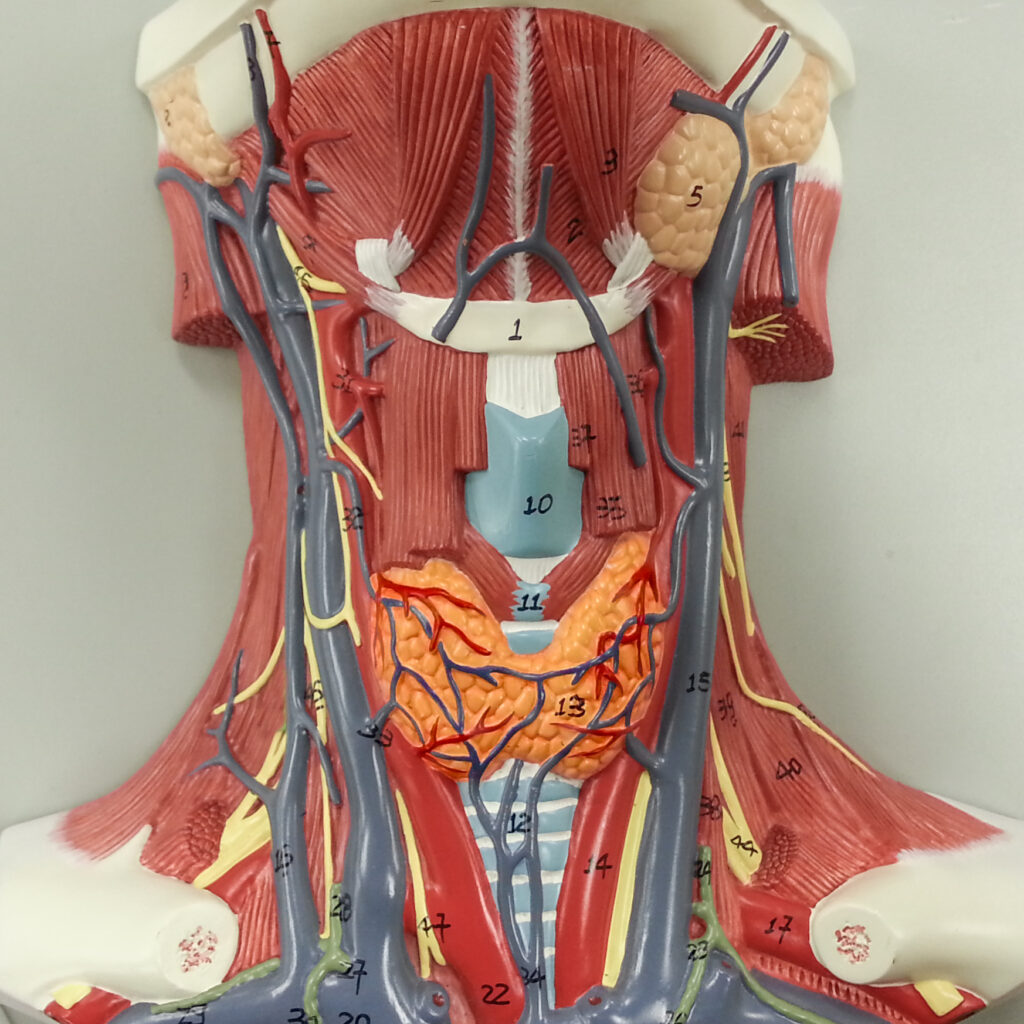
The thyroid gland is a small organ that’s located in the front of the neck, wrapped around the windpipe (trachea). It’s shaped like a butterfly, smaller in the middle with two wide wings that extend around the side of your throat.
Your thyroid creates and produces hormones that play a role in many different body systems. When your thyroid makes either too much or too little of these important hormones, it’s called a thyroid disease. There are several different types of thyroid disease, including hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, thyroiditis, and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
The thyroid is one of a number of endocrine glands that produce hormones to control the activity levels of many organ systems. Thyroid hormones like T3 and T4 tell the body’s tissues how much energy to use, to keep metabolism at an appropriate level. It also produces calcitonin which helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
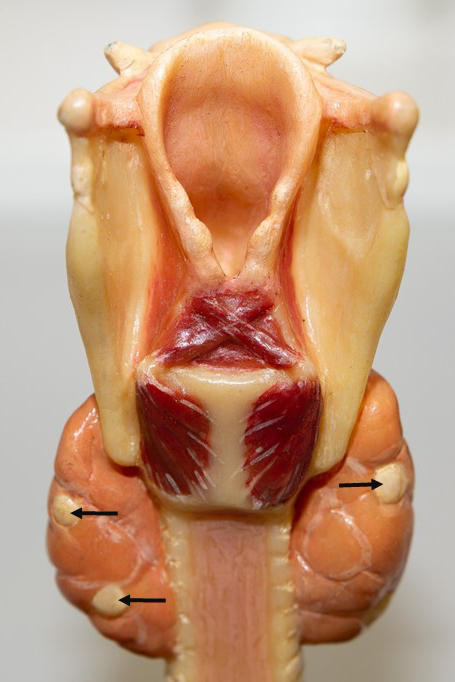
The parathyroid disease affects the parathyroid glands, four pea-sized bodies embedded in the posterior part of the thyroid gland. These glands produce parathyroid hormone (PTH), which helps maintain the correct levels of calcium in the body by opposing the action of calcitonin. Normally, the glands release just enough PTH to keep calcium levels normal. Disease states like hyper- and hypoparathyroidism and parathyroid cancer can disrupt this delicate balance.
more recommended stories
 Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for Physicians
Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for PhysiciansKey Takeaways Texas Medical Board has.
 Safer Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants with Treg Therapy
Safer Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants with Treg TherapyA new preclinical study from the.
 Autoimmune Disorders: ADA2 as a Therapeutic Target
Autoimmune Disorders: ADA2 as a Therapeutic TargetAdenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2) has emerged.
 Kaempferol: A Breakthrough in Allergy Management
Kaempferol: A Breakthrough in Allergy ManagementKaempferol, a dietary flavonoid found in.
 Early Milk Cereal Drinks May Spur Infant Weight Gain
Early Milk Cereal Drinks May Spur Infant Weight GainNew research published in Acta Paediatrica.
 TaVNS: A Breakthrough for Chronic Insomnia Treatment
TaVNS: A Breakthrough for Chronic Insomnia TreatmentA recent study conducted by the.
 First-of-Its-Kind Gene-Edited Pig Kidney: Towana’s New Life
First-of-Its-Kind Gene-Edited Pig Kidney: Towana’s New LifeSurgeons at NYU Langone Health have.
 Just-in-Time Training Improves Success & Patient Safety
Just-in-Time Training Improves Success & Patient SafetyA study published in The BMJ.
 ChatGPT Excels in Medical Summaries, Lacks Field-Specific Relevance
ChatGPT Excels in Medical Summaries, Lacks Field-Specific RelevanceIn a recent study published in.
 Study finds automated decision minimizes high-risk medicine combinations in ICU patients
Study finds automated decision minimizes high-risk medicine combinations in ICU patientsA multicenter study coordinated by Amsterdam.

Leave a Comment