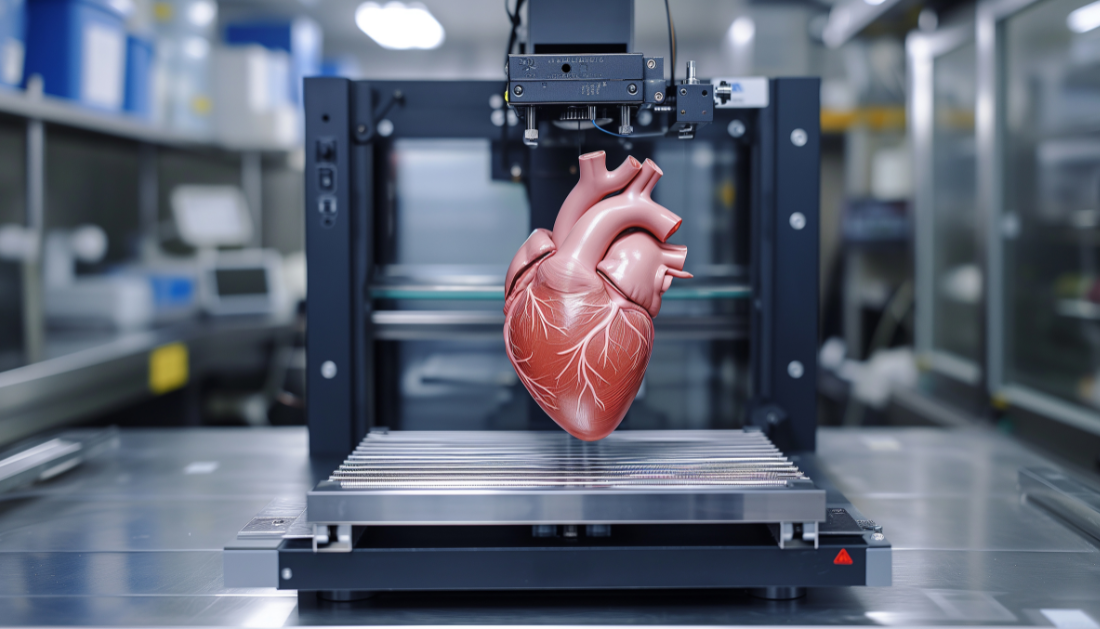

An international team of scientists from China and the United States has offered a thorough examination of the most recent developments in 3D bioprinting in a review that was recently published in Engineering. This cutting-edge technique has the potential to transform regenerative medicine and address some of the most important organ transplantation problems.
Organ failure or damage from disease, trauma, or aging presents a major problem because the body’s inherent capacity for regeneration is restricted. Despite saving lives, traditional organ transplantation is hampered by immunological rejection risk and a lack of donors. This has sparked a search for innovative remedies, and 3D organ bioprinting stands out as a potentially fruitful approach.
Modern bioprinting technologies are thoroughly examined in this review, with an emphasis on the cell types and bioinks that are essential for successful organ creation. The use of bioinks, which are crucial for building the intricate structures of organs, and the careful selection of suitable cells are crucial steps in the bioprinting process. The researchers examine the most recent developments in the bioprinting of several solid organs, such as the pancreas, liver, kidney, and heart. They stress how vital it is to vascularize—that is, to build the blood vessel network required for organ function—and integrate various cell types throughout the bioprinting process.
The review’s examination of the difficulties and potential paths forward for the therapeutic application of bioprinted organs is one of its main highlights. Although preclinical studies have demonstrated great promise for the technology, there are still major obstacles to be overcome before these results may be translated into clinical applications. The assessment emphasizes how important it is to do thorough testing and obtain regulatory approval in order to guarantee the dependability and safety of bioprinted organs. It is critical to guarantee that these organs are both patient-safe and highly functional.
The review covers ethical issues related to organ bioprinting in addition to technical difficulties. Examined are topics including cell source and the effects of altering human biology. It is a difficult task that requires considerable thought to strike a balance between these ethical issues and the revolutionary potential of bioprinting.
The evaluation presents a positive outlook for the future in spite of these obstacles. With the ability to produce customized replacement organs for each patient, bioprinting technology is viewed as a significant advancement in the biomedical sciences. This entails combining the intricate internal networks and blood arteries that are necessary for the proper operation of the organs in addition to accurately modeling their exterior architecture. These developments have the potential to drastically reduce the shortage of organs, offer individualized treatment plans, and completely change the fields of organ transplantation and personalized medicine.
A futuristic viewpoint on the potential for bioprinting to increase healthcare opportunities is presented in the review’s conclusion. The science of bioprinting is positioned to make substantial progress in better meeting patients’ demands by tackling both ethical and technical hurdles. This technology’s promise could completely change how we think about organ transplantation and personalized medicine, creating new avenues for patient care and treatment.
The knowledge gained from this review will be crucial in directing future organ bioprinting research and development as the field develops. The excitement surrounding this technology is a reflection of a common goal for a future in which patients worldwide will have access to individualized treatments and organ shortages will be mitigated.
For more information: Progress in Organ Bioprinting for Regenerative Medicine—Article. Engineering, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.04.023
more recommended stories
 Phage Therapy Study Reveals RNA-Based Infection Control
Phage Therapy Study Reveals RNA-Based Infection ControlKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) Researchers uncovered.
 Safer Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants with Treg Therapy
Safer Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants with Treg TherapyA new preclinical study from the.
 AI in Emergency Medicine and Clinician Decision Accuracy
AI in Emergency Medicine and Clinician Decision AccuracyEmergency teams rely on rapid, accurate.
 Innovative AI Boosts Epilepsy Seizure Prediction by 44%
Innovative AI Boosts Epilepsy Seizure Prediction by 44%Transforming Seizure Prediction in Epilepsy Seizure.
 Hypnosis Boosts NIV Tolerance in Respiratory Failure
Hypnosis Boosts NIV Tolerance in Respiratory FailureA New Approach: Hypnosis Improves NIV.
 Bee-Sting Microneedle Patch for Painless Drug Delivery
Bee-Sting Microneedle Patch for Painless Drug DeliveryMicroneedle Patch: A Pain-Free Alternative for.
 AI Reshapes Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation Care
AI Reshapes Anticoagulation in Atrial Fibrillation CareUnderstanding the Challenge of Atrial Fibrillation.
 Hemoglobin as Brain Antioxidant in Neurodegenerative Disease
Hemoglobin as Brain Antioxidant in Neurodegenerative DiseaseUncovering the Brain’s Own Defense Against.
 Global Data Resource for Progressive MS Research (Multiple Sclerosis)
Global Data Resource for Progressive MS Research (Multiple Sclerosis)The International Progressive MS Alliance has.
 AI Diabetes Risk Detection: Early T2D Prediction
AI Diabetes Risk Detection: Early T2D PredictionA new frontier in early diabetes.

Leave a Comment