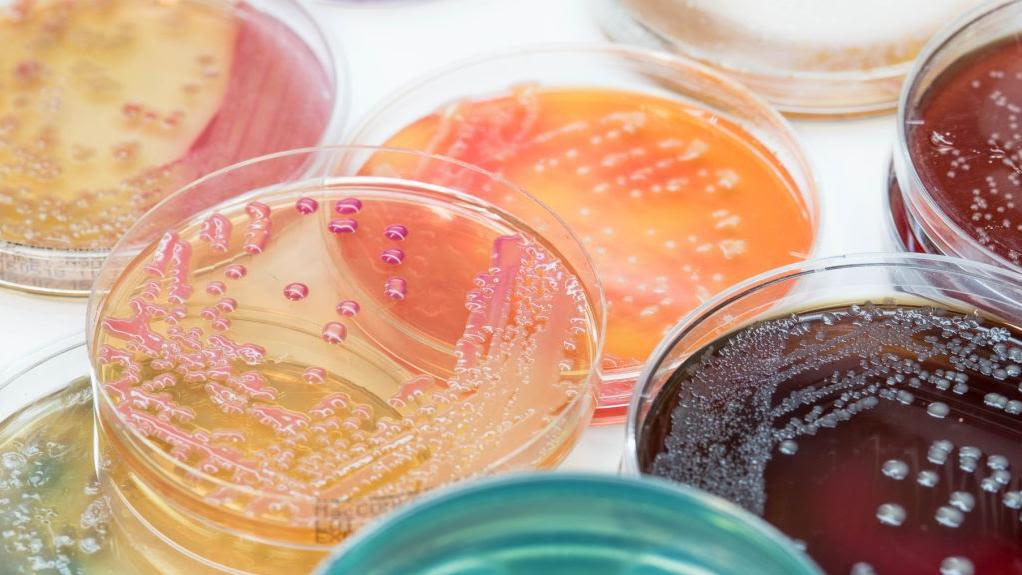

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) threatens the foundation of modern medicine and is described by the World Health Organization as one of the top global public health and development threats. It occurs when bacteria and other disease-causing microbes gain the ability to resist the action of treatments designed to kill them.
AMR has led to at least one million deaths each year since 1990 and is expected to cause another 39 million deaths between now and 2050. AMR is directly related to 16 of the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals, with severe negative implications for poverty, gender inequality, animal welfare, the environment, and food security.
In response to this far-reaching threat, the newly established Oxford AMR Network harnesses the University of Oxford’s considerable expertise in life sciences, medical and social sciences, and humanities to tackle this challenge through multiple approaches.
There are over 200 researchers working to tackle AMR across Oxford. Their work spans new drug discovery and antibiotic stewardship, to development of diagnostic tools and AMR surveillance and epidemiology.
Funded and hosted by the Ineos Oxford Institute for antimicrobial research (IOI), the network will mobilise Oxford University’s expertise in AMR to facilitate new collaborations and generate novel research to find solutions. A new database will list researchers across the university whose wide-ranging expertise exemplifies the vast array of world-leading research from Oxford teams, including overseas units in the MORU Tropical Health Network and the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit OUCRU).
more recommended stories
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.
 Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological Risk
Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological RiskKey Takeaways for HCPs Nanoplastics are.
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.

Leave a Comment