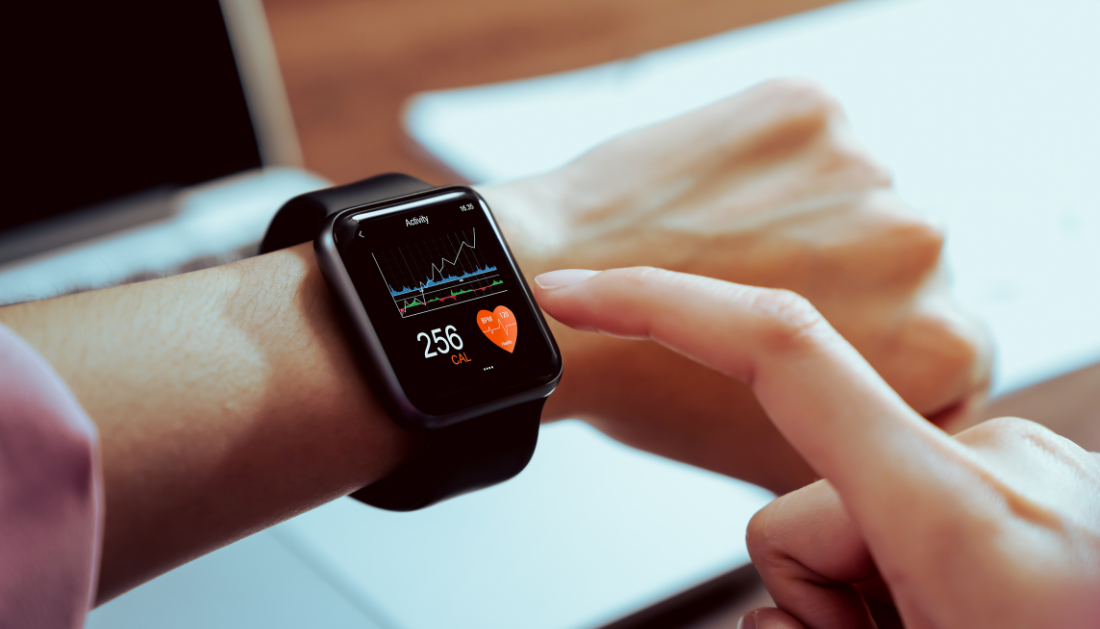


Modern technology enables individuals to monitor their heart health using devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and blood pressure monitors. However, a survey by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center reveals a crucial gap: while nearly two-thirds of Americans use these devices, only a quarter discuss their heart data findings with healthcare providers.
The national survey, involving 1,008 participants, found that smartwatches (32%), portable blood pressure monitors (31%), fitness apps (19%), and wearable trackers (13%) are the most popular tools. Despite the potential of these devices to detect issues like hypertension or irregular heart rhythms early, most users fail to share their data with doctors.
Dr. Laxmi Mehta, Director of Preventative Cardiology at Ohio State, stresses the value of self-monitoring devices in identifying problems early. For example, patterns of rising blood pressure or irregular heart rates can prompt timely consultations, preventing serious complications.
Sue VanWassenhove, a 78-year-old patient, exemplifies proactive health monitoring. Her smartwatch helped detect an unusual drop in heart rate, leading her to seek medical advice. During her visit, she discovered her smartwatch’s EKG feature, allowing her to share heart data directly with her cardiologist.
Dr. Mehta advises patients to pay attention to deviations in heart rate, which can result from conditions like dehydration, infections, or thyroid disorders, and consult a doctor when necessary. She also highlights the importance of regular exercise, recommending 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise weekly.
The study underscores the need to bridge the gap between heart health monitoring and communication with medical professionals. Sharing device data can empower individuals and healthcare providers to collaboratively manage heart health, fostering better long-term outcomes.
More Information: Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
more recommended stories
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NC
Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NCKey Highlights 15 confirmed Measles cases.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?
Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?Key Takeaways High-dose antioxidant supplementation in.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.
 Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New Study
Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New StudyKey Summary Cross-sectional analysis of 8,320.
 Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood Metabolites
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood MetabolitesKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) Researchers identified.
 Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge Drinking
Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge DrinkingKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Durvalumab in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Survival vs Cost
Durvalumab in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Survival vs CostKey Points at a Glance Durvalumab.

Leave a Comment