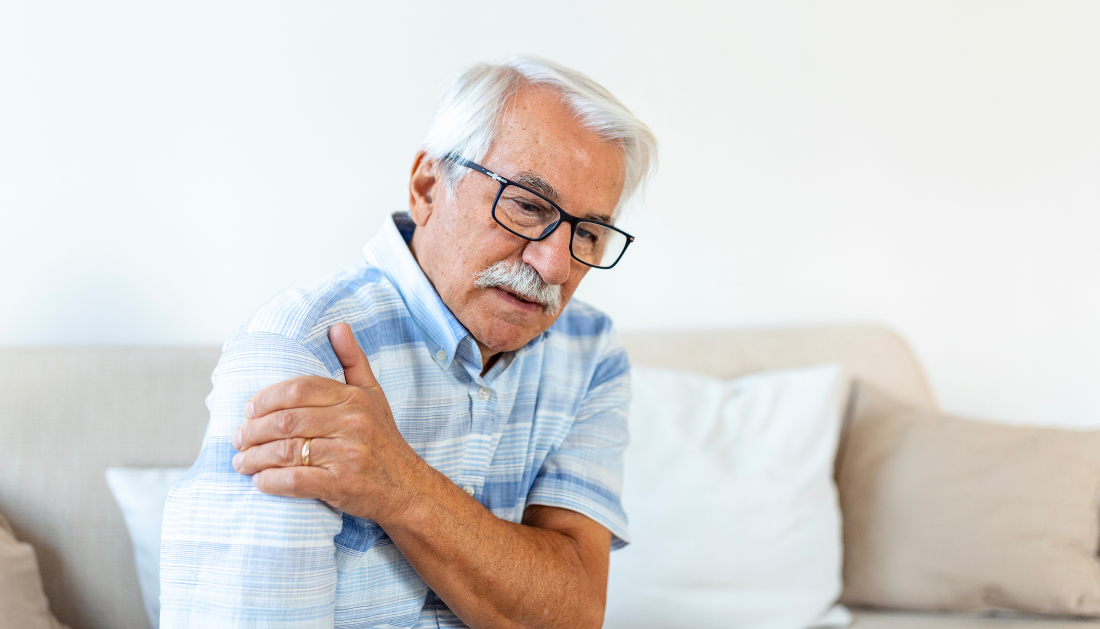


Nils Niederstrasser of the University of Portsmouth, UK, and colleagues released a new study in the open-access journal PLOS ONE this week that links frequent musculoskeletal pain to an increased chance of leaving employment and retiring earlier.
Previous research has found that patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain have greater rates of absenteeism, diminished working capacity, and lower incomes. Although the prevalence of musculoskeletal pain rises with age, little research has specifically examined the consequences of chronic pain on older people’s job status.
Niederstrasser and colleagues conducted the current study using data from 1,156 people aged 50 and up who lived in England and participated in the English Longitudinal Study of Aging. During the 14-year data gathering period, 1,073 people retired.
The researchers discovered that people with higher musculoskeletal pain complaints retired earlier than pain-free participants (HR = 1.30, CI = 1.12-1.49). Participants with pain were also 1.25 times more likely to leave work sooner (CI = 1.10–1.43), regardless of whether they identified as retired.
Other characteristics related to an earlier retirement age included increased work discontent and self-perceived social standing. Even after controlling for job satisfaction, depressive symptoms, self-perceived social status, sex, and working circumstances, frequent musculoskeletal discomfort remained a significant predictor of premature retirement and work discontinuation.
The authors conclude that pain experiences can contribute to poor work outcomes and point out that further study should determine the mechanisms and decision making involved in quitting the profession for those with recurrent musculoskeletal pain.
The authors write, “It is remarkable that pain predicts earlier retirement and work cessation to the same extent, if not more strongly, than other variables, such as job satisfaction or specific job demands.” It demonstrates how much suffering may affect many facets of people’s lives.”
More information: Musculoskeletal pain affects the age of retirement and the risk of work cessation among older people, PLoS ONE (2024). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297155
more recommended stories
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV Tumors
Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV TumorsKey Highlights Reconfiguring peptide orientation significantly.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for Neuroprotection
Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for NeuroprotectionKey Highlights A Phase III clinical.
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.
 Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social Media
Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social MediaKey Summary Anxiety commonly begins in.
 Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in Cancer
Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in CancerKey Takeaways Johns Hopkins researchers developed.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.
 Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy Success
Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy SuccessKey Summary Spanish researchers report complete.
 Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life Experience
Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life ExperienceKey Takeaway Summary Immune cell responses.

Leave a Comment