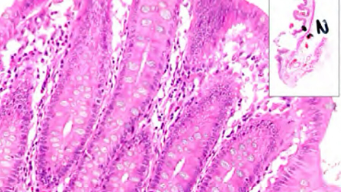

The research addresses the long-recognized poor prognosis of relatively undifferentiated cancers, suggesting that selection against differentiation and in favour of uncontrolled growth is a powerful driver of cancer progression. Goblet cells, which provide the mucous surface of the gut, are a crucial focus of this study. When present in colorectal cancers, these cancers are termed mucinous.
Key findings from the study include:
- Nearly 80 CRC-derived cell lines are classified into five categories based on the levels of MUC2 (the main mucous product of goblet cells) and TFF3 (an associated gene product).
- Identification of five distinct patterns of MUC2 and TFF3 expression, which can be easily identified in tumour specimens, allowing for a finer characterisation of CRCs concerning goblet cell differentiation.
- It was discovered that approximately 30% of all CRCs express TFF3 but not MUC2, a previously unrecognised subgroup.
- Highlighting the role of LGR5 in controlling differentiation rather than direct control of cell growth, challenging previous assumptions.
more recommended stories
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.
 Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological Risk
Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological RiskKey Takeaways for HCPs Nanoplastics are.
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.

Leave a Comment