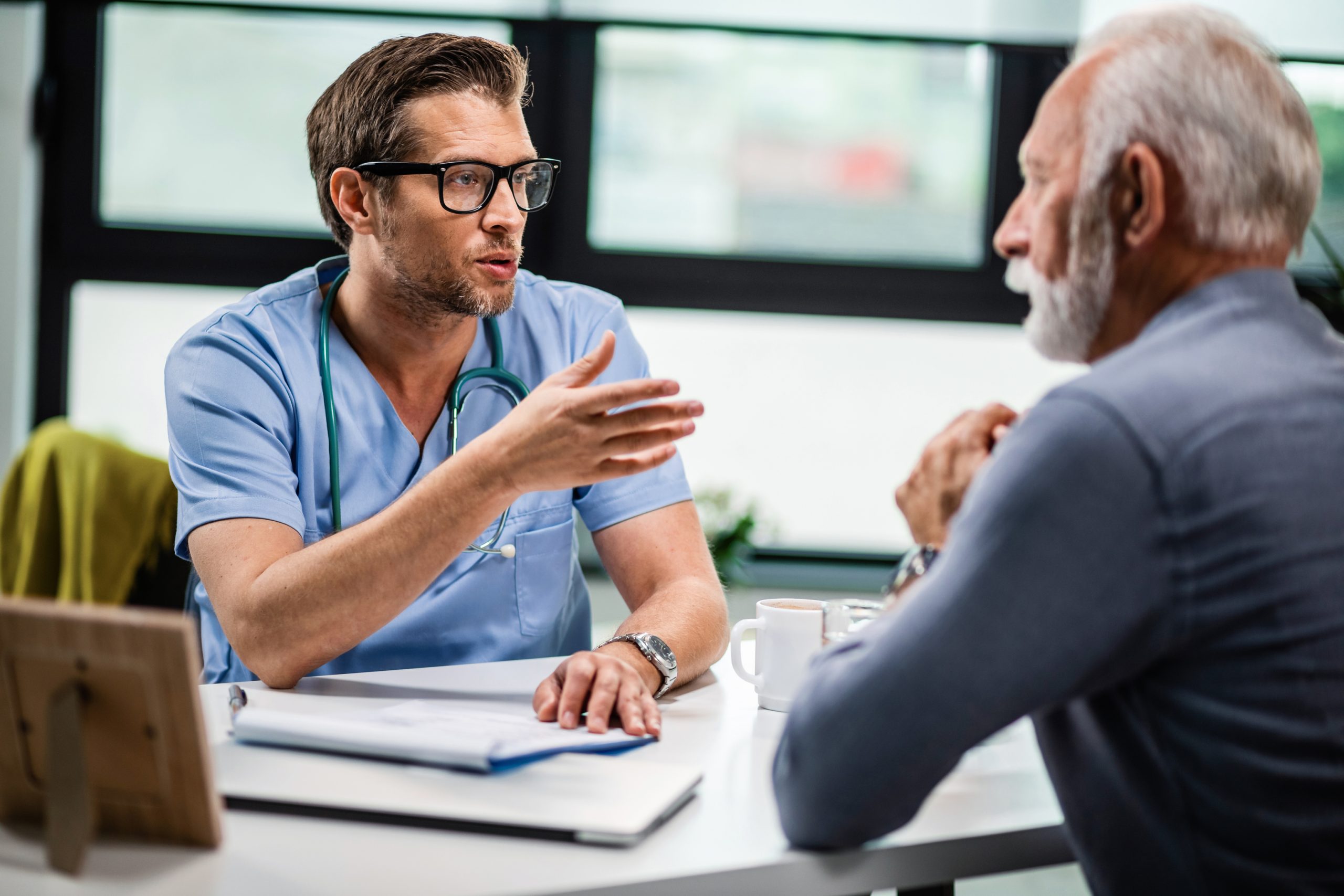


The study, funded by the National Institute of Health and Care Research Bristol Biomedical Research Centre (NIHR Bristol BRC), is one of the first to look at these issues and see what patients are told about new surgical techniques. While surgical innovation is critical to improving outcomes, an independent safety study led by Baroness Cumberlege found that patients may not be receiving all of the information they require prior to having new treatments. According to current recommendations, patients should be provided adequate information by the surgeons to properly weigh the risks and advantages of a new procedure.
The study team examined consultations between surgeons and patients in which new procedures were discussed in order to analyze current practice. They concentrated on seven different procedures being implemented in five NHS institutions. In addition, nine clinicians performing novel procedures were interviewed about what they wished to tell patients.
Researchers discovered that practitioners intended to convey the novel nature of the procedures but acknowledged that these discussions sometimes be difficult. The researchers audio-recorded 37 meetings between clinicians and patients in which novel procedures were mentioned.
Only a minority of clinicians clearly mentioned the procedure as innovative, their limited expertise with it, a lack of proof, and doubt regarding the outcome. The study also found that while all practitioners were excited about the benefits of a new type of operation, they frequently failed to disclose the possible hazards.
Thirty post-operative interviews with patients were then undertaken. This was done by researchers to learn what patients thought about the information they were given.
Patients had a great sense of trust in their clinicians and were reassured by their confident demeanor. They also picked up on clinicians’ enthusiasm for operations they saw as “future-proof.” Many people believed the procedures were more established than they were, and they felt they were not informed about the potential downsides of undergoing the new operation.
Dr Daisy Elliott, lead author and Research Fellow in the Bristol Medical School: Population Health Sciences (PHS), said: “This study provides important insights into the communication process surrounding innovative surgical procedures and devices. Despite the clinicians’ best intentions, many patients weren’t fully informed about innovative procedures. Whilst there is often a belief that ‘new is better’, this research highlights that clinicians can find it difficult to provide neutral and balanced information in this context. A major focus of our work at the Bristol BRC will be to work with clinicians to provide support and training, so that patients can make well informed decisions about undergoing new procedures.”
Paula Goss, founder of Rectopexy mesh victims and support and ambassador for Mesh UK, added: “Fully informed consent discussions are crucial for patient safety for all procedures. Consultants and nurses should speak to patients thoroughly and transparently, allow recording of the consultations for patients to think about the information provided, and patients should be able to continue a dialogue to ask any question before any procedure. This should be a mandatory requirement for all hospitals and healthcare settings. Thorough in-depth patient involvement at every stage is the only way to provide and correct the issue of lack of trust that arises commonly with patients about to undergo any procedure.”
Jane Blazeby, Professor of Surgery in the Bristol Medical School: (PHS) and project lead, said: “To our knowledge this is the first time that conversations between clinicians and patients discussing innovative surgical procedures have been investigated. It highlights the need for a standard approach that provides clear and unbiased information for patients. This is our next plan to improve this process to benefit patients, surgeons and the NHS.”
more recommended stories
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.
 Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological Risk
Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological RiskKey Takeaways for HCPs Nanoplastics are.
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV Tumors
Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV TumorsKey Highlights Reconfiguring peptide orientation significantly.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for Neuroprotection
Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for NeuroprotectionKey Highlights A Phase III clinical.
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.
 Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?
Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?Key Takeaways High-dose antioxidant supplementation in.

Leave a Comment