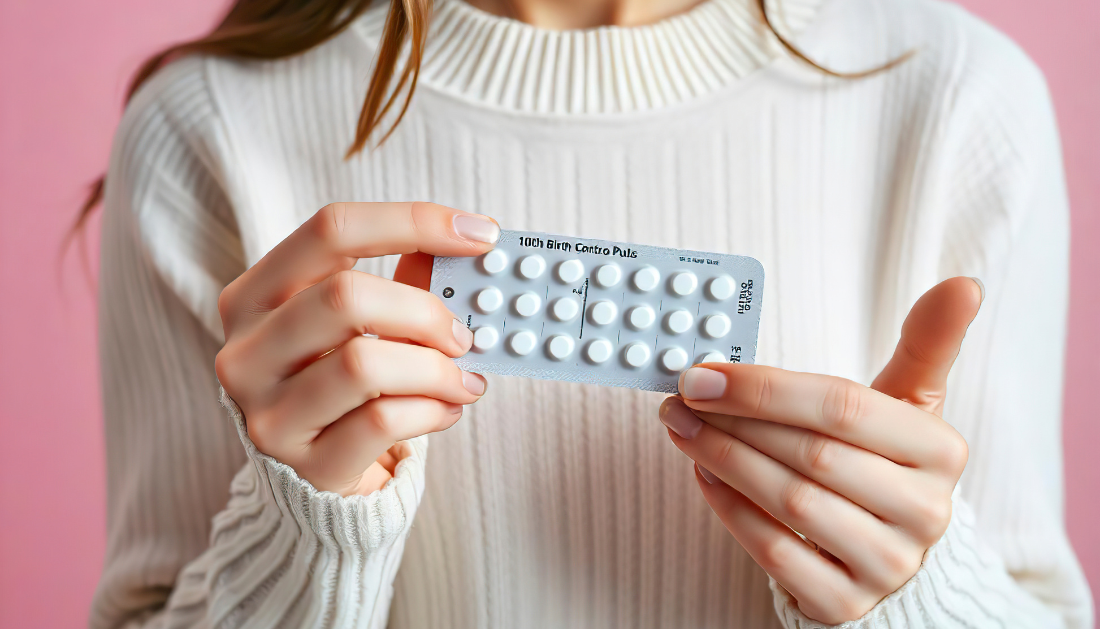


In a new study published in Nutrients, researchers used a randomized crossover design to explore the effect of the combination oral contraceptive pill (OCP) on the postprandial glycemic response to an oral glucose bolus in healthy young women.
Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a group of illnesses that include hypertension, dyslipidemia (abnormal blood cholesterol levels that raise cardiovascular risk), impaired glucose metabolism, and abdominal obesity. These symptoms all increase the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, which are now considered a global epidemic.
The prevalence of MetS in women, particularly those of childbearing age, is increasing faster than in males, contributing to greater rates of cardiometabolic illnesses. Between 1988-1994 and 2007-2012, the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) found that the prevalence of MetS in women increased significantly from 25% to 34.9%.
Despite extensive use, OCP’s metabolic effects remain unknown, necessitating additional research into its impact on women’s cardiometabolic risk.
About the study
The study included healthy young women aged 18-40 with a BMI ranging from 18.5 to 26.9 kg/m² who had been using a combination monophasic OCP for over 3 months. A priori power analysis determined that a sample size of 16 would be sufficient to detect a significant change in fasting blood glucose.
To account for anticipated dropouts, 22 women were initially enrolled, 18 of whom completed both study visits. Preliminary findings revealed differences in glucose homeostasis based on pill type (androgenic or anti-androgenic), necessitating the recruitment of three extra subjects taking anti-androgenic tablets to establish a sufficient subgroup size for comparison.
Significant weight changes in the previous six months, irregular withdrawal bleeding, chronic medical disorders, and the use of metabolism-altering drugs were also excluded.
Vegetarians, vegans, and those who are claustrophobic were also excluded due to secondary study effects including energy metabolism. The study was authorized by the Northern Health and Disability Ethics Committee and followed the Declaration of Helsinki.
Prior to each visit, participants ate a standardized diet and avoided caffeine, alcohol, and strenuous physical activity. Each visit comprised blood sampling before and after a glucose drink, which were then collected and processed for various metabolic studies.
Statistical methods were used to compare glucose homeostasis and hormonal profiles across OCP periods and pill kinds.
Conclusions
To summarize, in this study, women who used oral contraceptives containing androgenic progestogens had significantly higher postprandial glucose, insulin, and C-peptide levels, with iAUC increases of approximately 100%, 50%, and 42%, respectively, during the active phase compared to the inactive phase.
This shows that androgenic OCPs could reduce glucose tolerance and promote insulin resistance. Similar investigations found increases in glucose and C-peptide but decreased insulin levels, indicating improved hepatic insulin clearance.
However, in this investigation, greater insulin secretion was found without commensurate increases in clearance, resulting in persistently raised insulin levels.
For more information: The Effect of the Oral Contraceptive Pill on Acute Glycaemic Response to an Oral Glucose Bolus in Healthy Young Women: A Randomised Crossover Study, Nutrients, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16203490
more recommended stories
 Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge Drinking
Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge DrinkingKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Precision Oncology with Personalized Cancer Drug Therapy
Precision Oncology with Personalized Cancer Drug TherapyKey Takeaways UC San Diego’s I-PREDICT.
 Iron Deficiency vs Iron Overload in Parkinson’s Disease
Iron Deficiency vs Iron Overload in Parkinson’s DiseaseKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis Insights
Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis InsightsKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) A Clinical.
 Silica Nanomatrix Boosts Dendritic Cell Cancer Therapy
Silica Nanomatrix Boosts Dendritic Cell Cancer TherapyKey Points Summary Researchers developed a.
 Vagus Nerve and Cardiac Aging: New Heart Study
Vagus Nerve and Cardiac Aging: New Heart StudyKey Takeaways for Healthcare Professionals Preserving.
 Cognitive Distraction From Conversation While Driving
Cognitive Distraction From Conversation While DrivingKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) Talking, not.
 Fat-Regulating Enzyme Offers New Target for Obesity
Fat-Regulating Enzyme Offers New Target for ObesityKey Highlights (Quick Summary) Researchers identified.
 Spatial Computing Explains How Brain Organizes Cognition
Spatial Computing Explains How Brain Organizes CognitionKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) MIT researchers.
 Gestational Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood Metabolites
Gestational Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood MetabolitesKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for Clinicians).

Leave a Comment