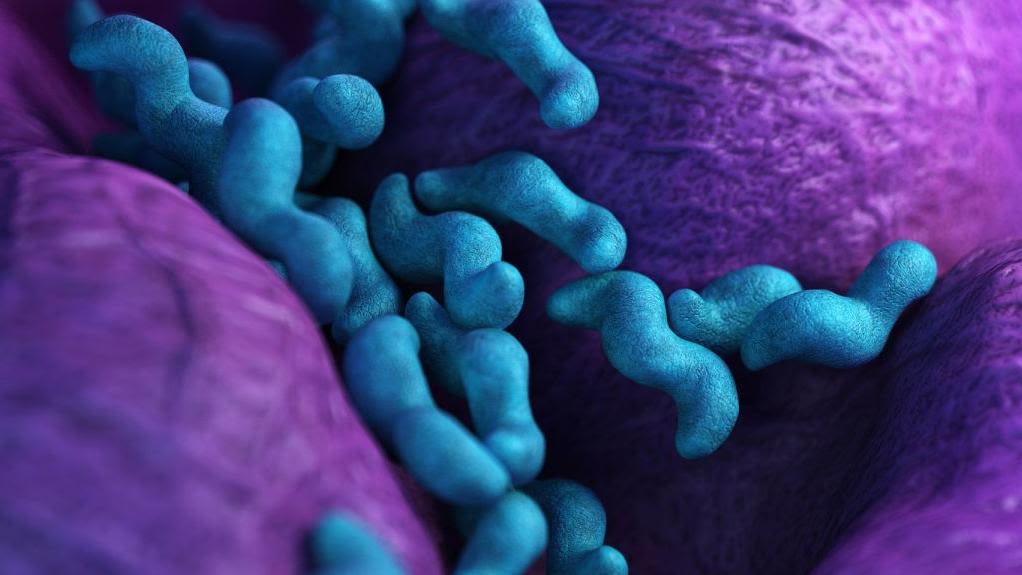

Diarrhoeal disease is responsible for killing around 444,000 children every year, mainly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). Worryingly, antibiotics are becoming increasingly ineffective against the bacteria that cause diarrhoea as these evolve to resist the action of these medicines.
An international collaboration led by Professor Sheppard will tackle this challenge by creating a framework of meta-genomic epidemiology surveillance. This advanced approach is used to monitor and track the spread of infectious diseases by analysing the genetic material of all microorganisms present in a sample, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. The aim is to apply the genetic data to develop a vaccine for livestock: one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of antibiotic-resistant diseases.
This work will focus on Campylobacter, the most common bacterial cause of diarrhoea. These bacteria are prevalent in livestock such as poultry, cattle, pigs, and sheep and can be transmitted to humans via contaminated water and food. The research team will study the genetic make-up of Campylobacter populations recovered from hospital and farm sites, and use these data to develop a vaccine for animals that will interrupt the transmission chain and prevent the spread of Campylobacter to humans.
Pilot research has already taken place in The Gambia, Burkina Faso, Ghana and Peru. With the new funding, the team will further expand this work across Africa, where local partners will collect samples from infected humans and children, wild and domesticated animals, retail meat from supermarkets, and the natural environment (such as waterbodies).
Professor Sam Sheppard, Principal Investigator, Ineos Oxford Institute for antimicrobial research, said: ‘Contemporary meta-genomic epidemiology techniques will help us understand cryptic disease networks and track how the disease is transmitted from animals to humans. Working in partnership with a network of 19 countries and nine African Co-investigators, the Wellcome Discovery Award will allow us to create a global genomic surveillance hub to track the spread of diarrhoeal diseases.’
Read the full story on the University of Oxford website.
more recommended stories
 Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety Concerns
Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety ConcernsKey Summary Experts publishing in The.
 Oligometastatic Pancreatic Cancer: New Global Consensus
Oligometastatic Pancreatic Cancer: New Global ConsensusKey Points Summary An international expert.
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US States
Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US StatesKey Points Researchers developed a new.
 Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic Type
Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic TypeKey Summary A new study from.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.

Leave a Comment