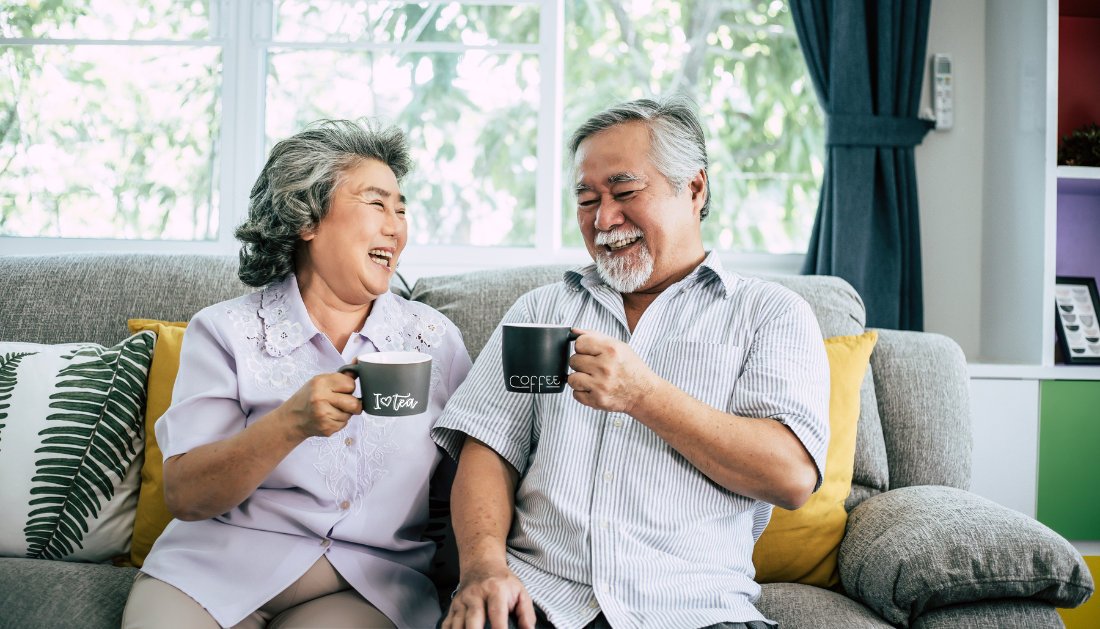


Coffee and cognitive performance linked to fluid intelligence
A large UK-based longitudinal study highlights the potential role of moderate coffee and tea intake in maintaining brain health among seniors. Tracking 8,700 participants aged 60–85 over nine years, researchers found that moderate coffee consumption and both moderate and high tea intake were associated with slower cognitive decline in seniors, particularly in fluid intelligence, the reasoning and problem-solving abilities that often diminish with age.
Explore All Geriatrics CME/CE Conferences
Cognitive assessments measured numeric reasoning, visual memory, and reaction time while accounting for genetic factors such as Apolipoprotein E genotype and lifestyle variables. Moderate coffee drinkers demonstrated better preservation of reasoning skills compared to high coffee consumers, suggesting that beyond three cups per day, benefits may plateau or reverse.
Tea and brain health: antioxidants and polyphenols at play
For tea, both moderate and high consumption correlated with slower declines in cognitive performance. Researchers point to compounds such as catechins in tea, theanine effects, and a mix of antioxidants in coffee and tea that may protect neural pathways through anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective mechanisms.
The findings align with prior data suggesting moderate intake of these beverages could aid in dementia prevention and reduce Alzheimer’s disease risk, though further randomized controlled trials are needed. The study also highlights the role of polyphenols and brain health, indicating that the combination of caffeine and bioactive plant compounds may synergistically support cognitive resilience.
Clinical implications for healthcare professionals
For HCPs, these findings have direct relevance to preventive care in aging populations. The link between caffeine and cognitive function provides an accessible lifestyle factor to discuss with patients at risk of cognitive decline in seniors. Incorporating guidance on moderate coffee and tea consumption into dietary counseling may complement broader interventions for brain health, particularly in neurology and geriatrics.
Nurses and primary care providers engaged in patient education can use these insights to shape personalized nutrition recommendations. Emphasizing moderation is key: around one to three cups of coffee per day, combined with regular tea intake, appears to offer the strongest benefits without the potential downsides of high caffeine exposure.
Importantly, the study’s longitudinal cognitive assessment adds weight to these findings, offering nearly a decade of follow-up data. This provides clinicians with a more robust evidence base than shorter observational studies. While individual tolerance and comorbidities must always be considered, the results reinforce that modest adjustments to everyday beverage habits can be a low-risk, potentially protective strategy for maintaining fluid intelligence and delaying cognitive aging.
For More Information:
Rainey-Smith, S. R., Sewell, K. R., Brown, B. M., Sohrabi, H. R., Martins, R. N., & Gardner, S. L. (2025). Moderate coffee and tea consumption is associated with slower cognitive decline. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease. DOI: 10.1177/13872877251361058, https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/13872877251361058
more recommended stories
 Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat Diet
Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat DietKey Points A high-fat diet accelerated.
 Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA Analysis
Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA AnalysisKey Takeaways Serial liquid biopsies using.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain Changes
Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain ChangesKey Takeaways Brain vascular health is.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?
Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?Key Takeaways High-dose antioxidant supplementation in.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.

Leave a Comment