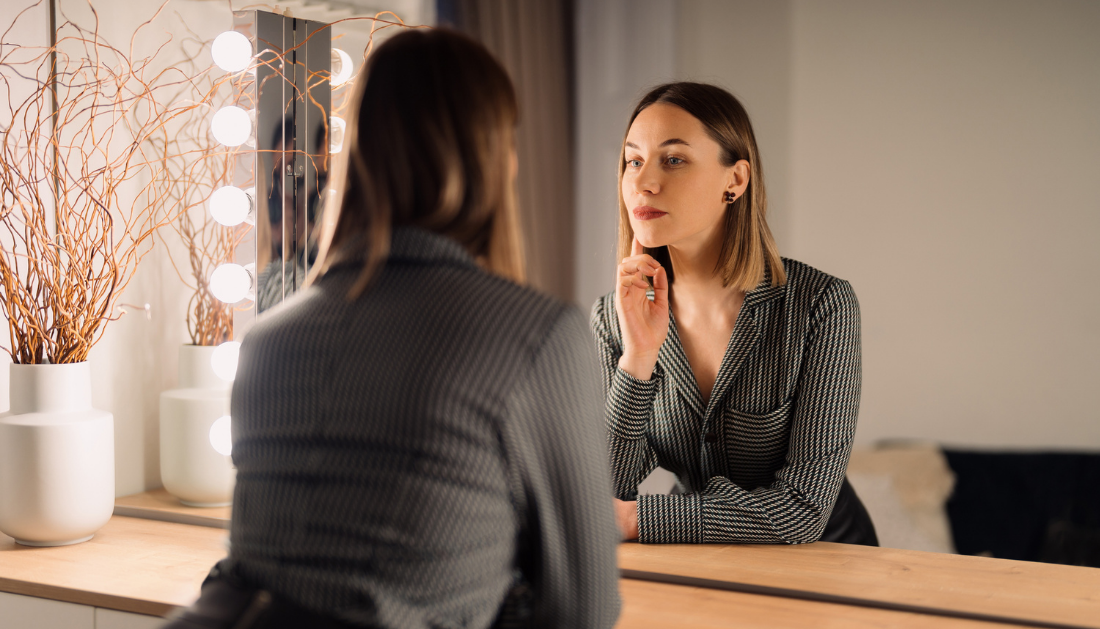


Narcissism has been identified as a factor linked to a less favorable response to psychotherapy treatment. This conclusion stems from a comprehensive multi-site German study encompassing more than 2,000 patients undergoing inpatient and outpatient psychotherapy. The research findings from the collaborative team at Jena University Hospital and the University of Münster, recently featured in the esteemed scientific journal The Lancet Psychiatry, offer valuable insights that could contribute to the refinement of personalized psychotherapy approaches.
A narcissist is a person who, like Narcissus in Greek mythology, has an excessive feeling of grandiosity and entitlement. A team of researchers from Jena University Hospital and the University of Münster evaluated how narcissistic traits affect the treatment of mental health concerns in a Germany-wide study with over 2,000 patients from inpatient and outpatient psychotherapy. To that goal, the researchers measured the individuals’ narcissistic personality traits and depressive symptoms before and after treatment with two distinct psychotherapy methods.
The study team discovered that in both groups, strong narcissistic rivalry is connected with more severe depressive symptoms prior to the commencement of therapy. In contrast, the desire to be adored was associated with a lower level of depression intensity. The study’s key findings are summarized as follows by Maike Richter, the study’s first author: “In the group of patients treated with cognitive behavioral therapy, narcissism was associated with a poorer response to treatment, even when a narcissistic personality disorder was not fully developed.” The rivalry dimension, in particular, had a negative impact.
Narcissism has an impact on therapeutic relationships
However, no harmful impacts of narcissism on treatment response were discovered in patients receiving psychoanalytic-interactional therapy, which was established expressly for those experiencing difficulties in interpersonal relationships. The researchers believe that the difference in treatment strategies was caused by interpersonal behavior patterns between the patient and the therapist. Further research supports this concept, according to Prof. Nils Opel of Jena University Hospital: “We found evidence that the negative effects of narcissism are based on a weaker therapeutic relationship.”
The findings, according to the authors, make an essential contribution to the understanding of narcissistic personality traits and their involvement in the treatment of mental disorders in general. “Narcissism can be a relevant factor for mental health, leading to psychotherapy being less effective,” says Prof. Mitja Back of the University of Münster. As a result, the researchers advise therapists to carefully analyze their patients’ narcissistic tendencies and to pay special attention to the therapeutic connection.
more recommended stories
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV Tumors
Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV TumorsKey Highlights Reconfiguring peptide orientation significantly.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for Neuroprotection
Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for NeuroprotectionKey Highlights A Phase III clinical.
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.
 Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social Media
Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social MediaKey Summary Anxiety commonly begins in.
 Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in Cancer
Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in CancerKey Takeaways Johns Hopkins researchers developed.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.
 Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy Success
Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy SuccessKey Summary Spanish researchers report complete.
 Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life Experience
Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life ExperienceKey Takeaway Summary Immune cell responses.

Leave a Comment