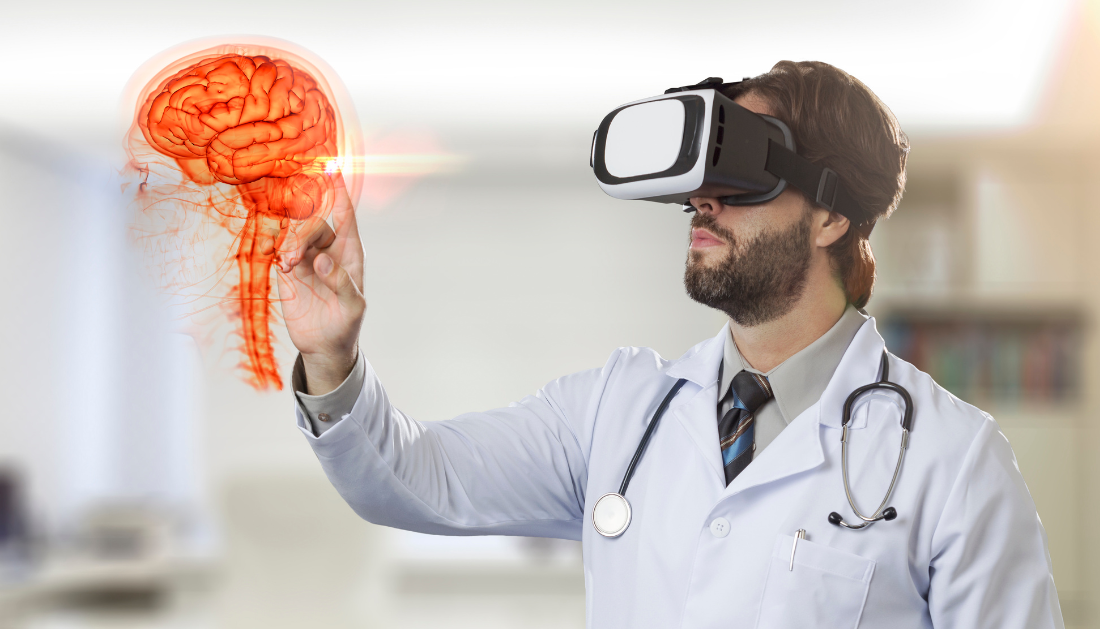

DELiVR is a novel AI-based method that researchers at Helmholtz Munich and the LMU University Hospital Munich present to tackle the challenging issue of brain cell mapping. The journal Nature Methods publishes the findings.
The deep learning technology removes the barrier of coding expertise, democratizing advanced neuroscience. DELiVR enables biologists to effectively study spatial cell dynamics associated with disease, which promotes the creation of precision medicines for improved patient care.
For more details and to register for Neurology insights, check out Global Neurology Summit 2024.
Making 3D Brain Analysis more accessible
Variations in the brain’s expression of specific proteins have been connected to a number of disorders. Scientists use model organisms to explore the changes in certain parameters as diseases progress. Large-scale data sets are produced by imaging whole mouse brains, which makes precise quantification techniques necessary for its meaningful interpretation. It is difficult to locate tagged cells in massive 3D picture datasets, though.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has great potential for data analysis, but its application is usually limited to specialist labs due to the high level of coding expertise and data annotation required. Therefore, the goal of the study team was to get beyond these obstacles and democratize 3D analysis for wider scientific access.
Researchers are empowered by Virtual Reality
The study team first trained an AI algorithm to recognize particular cells in 3D microscopic images in order to precisely measure those cells within brain imaging. The researchers used virtual reality (VR) to create labels by fully submerging themselves in the pictures and directly labeling cells in three dimensions (three dimensions being faster and more accurate than two dimensions slice-based methods).
The researchers then used these VR-generated labels to train an AI system that would recognize activated neurons automatically. They incorporated into their DELiVR (Deep Learning and Virtual Reality mesoscale annotation) pipeline the procedures of cell detection, matching, and visualization concerning a brain atlas.
In an end-to-end process, the system works flawlessly with Fiji, an open-source image analysis program. DELiVR’s versatility for a variety of research projects is further demonstrated by its customizable function, which enables researchers to train it for certain cell types, such as microglia, an important immune cell in the brain.
“In essence, DELiVR offers a seamless solution for identifying and analyzing cells throughout the entire brain, providing invaluable insights into their roles and behaviors in both health and disease—all without requiring coding expertise from scientists. DELiVR represents a step towards developing new therapeutic interventions that could ultimately improve the quality of life for individuals affected by debilitating conditions,”claims Prof. Ali Ertürk, who oversaw the tool’s development at Helmholtz Munich.
Use case: Loss of weight due to Cancer
The research team used DELiVR to illustrate how powerful it is and how it can change our understanding of how cancer affects our brain activity. They focused on the important clinical problem of tumor-induced weight loss and found distinct patterns of brain activity that differentiate malignancies that cause weight loss in mice from those that do not.
The first author of the study establishing DELiVR, Dr. Doris Kaltenecker, states, “Our findings using DELiVR have revealed potential therapeutic targets within brain regions. This might pave the way for promising strategies to combat cancer-related weight loss in the future.”
For more information: Virtual reality-empowered deep-learning analysis of brain cells, Nature Methods, DOI: 10.1038/s41592-024-02245-2
more recommended stories
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV Tumors
Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV TumorsKey Highlights Reconfiguring peptide orientation significantly.
 Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NC
Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NCKey Highlights 15 confirmed Measles cases.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Chronic Brain Compression Triggers Neuron Death Pathways
Chronic Brain Compression Triggers Neuron Death PathwaysKey Takeaways Chronic brain compression directly.
 Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for Physicians
Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for PhysiciansKey Takeaways Texas Medical Board has.
 Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for Neuroprotection
Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for NeuroprotectionKey Highlights A Phase III clinical.
 Needle-Thin Brain Implant for Layer-Specific Brain Research
Needle-Thin Brain Implant for Layer-Specific Brain ResearchKey Takeaways Researchers have developed a.
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.

Leave a Comment