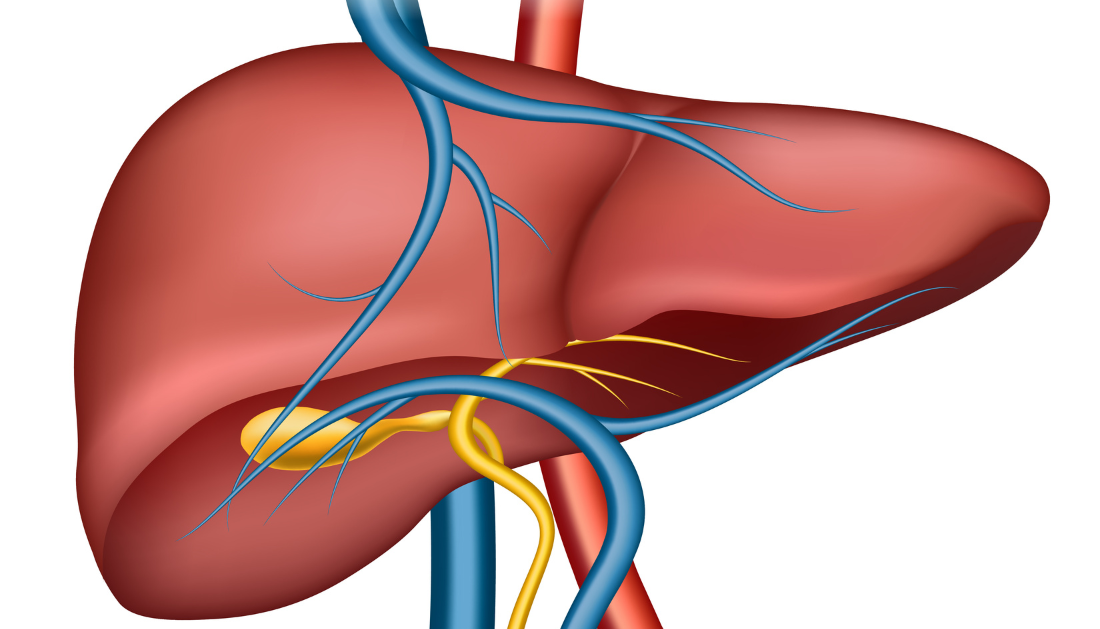

Ischemic cholecystitis is a type of gallbladder inflammation that develops in the absence of gallstones or other external pressures. It is caused by a lack of blood flow to the gallbladder tissue.
This new study is significant because it contributes to a better understanding of the pathogenesis of ischemic cholecystitis and the development of more effective treatments for this ailment.
A study was done by a team of researchers from the University of California, San Francisco, to investigate the cause of this condition. They discovered that the gallbladder is particularly vulnerable to ischemia because it receives its blood supply from a terminal artery, which means that if this artery becomes blocked, there is no other artery to deliver blood to the gallbladder.
The researchers also discovered that ischemic cholecystitis is more likely in severely unwell patients. This is because critically ill individuals are frequently hypovolemic, or have low blood volume. This can result in decreased gallbladder perfusion, which can cause inflammation.
These findings have substantial implications for ischemic cholecystitis diagnosis and treatment. This is sometimes misinterpreted as another ailment, such as sepsis or pancreatitis, due to its difficulty in diagnosis. This can result in therapy delays and lower patient outcomes.
The researchers also discovered that ischemic cholecystitis recurs more frequently than obstructive cholecystitis. This means that patients with ischemic cholecystitis are more likely to undergo gallbladder removal operations.
The gallbladder is surgically removed to treat this condition. This is the only way to keep the condition from coming back.
Ischaemic cholecystitis is a rare but deadly illness that is more common in critically unwell people. Clinicians must be aware of this disorder to diagnose and treat it as soon as possible.
For more information: Favela, J. G., et al. (2023). Aetiology, diagnosis and management for ischaemic cholecystitis: current perspectives. eGastroenterology. doi.org/10.1136/egastro-2023-100004.
more recommended stories
 Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety Concerns
Invasive Cosmetic Procedures Raise Patient Safety ConcernsKey Summary Experts publishing in The.
 Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent Allergies
Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent AllergiesKey Summary Researchers at Stanford University.
 Oligometastatic Pancreatic Cancer: New Global Consensus
Oligometastatic Pancreatic Cancer: New Global ConsensusKey Points Summary An international expert.
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US States
Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US StatesKey Points Researchers developed a new.
 Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic Type
Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic TypeKey Summary A new study from.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.

Leave a Comment