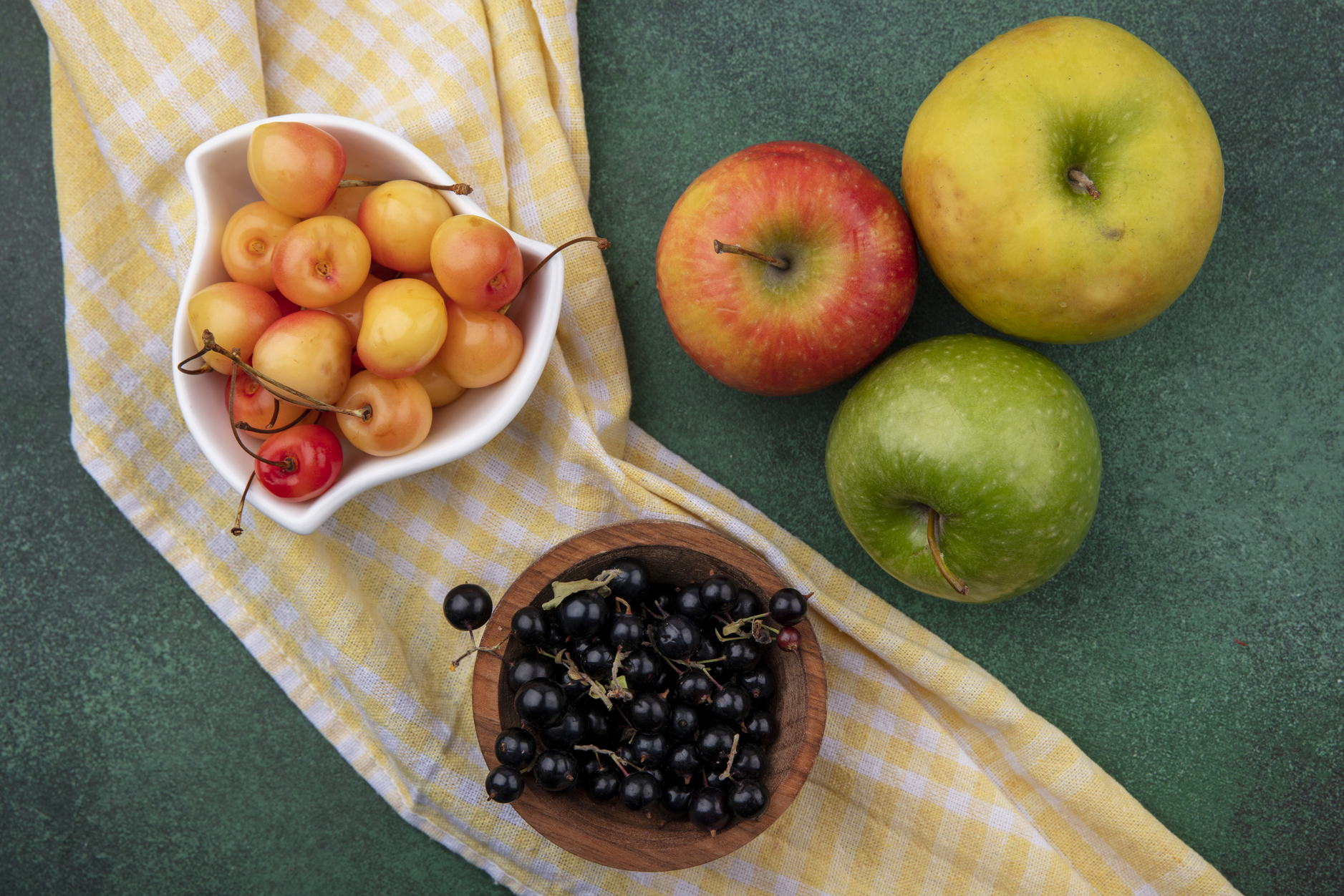


Eating plant-based meals high in flavonols, which are nutritional chemicals, can reduce your risk of developing frailty. Foods containing flavonoids called quercetin, such as apples and blackberries, may be the most significant for frailty prevention.
Frailty, a geriatric syndrome that increases the risk of falls, fractures, disability, hospitalization, and mortality, affects 10% to 15% of older persons. Protein consumption is the primary emphasis of current dietary advice for frailty prevention. However, there are numerous additional foods that may be beneficial to one’s health.
“There may be some validity to the old saying, an apple a day keeps the doctor (or frailty) away,” said the authors. “Our findings suggest that for every 10 mg higher intake of flavonols per day, the odds of frailty were reduced by 20%. Individuals can easily consume 10 mg of flavonols intake per day since one medium sized apple has about 10 mg of flavonols.”
“Although there was no significant association between total flavonoid intake and frailty, higher flavonols intake (one of the subclasses of flavonoids) was associated with lower odds of developing frailty. Specifically, higher quercetin intake was the flavonoid that had the strongest association with frailty prevention. This data suggests that there may be particular subclasses of flavonoids that have the most potential as a dietary strategy for frailty prevention,” said co-author Shivani Sahni, Ph.D., of Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, and the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife; and Courtney L. Millar, Ph.D., of the Department of Medicine, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, and the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research, Hebrew SeniorLife.
Future study should focus on dietary therapies with flavonols or quercetin for the treatment of frailty, according to the authors. There is also a need for research with racially and ethnically diverse subjects.
The findings were published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition article, “Higher Intake Of Dietary Flavonols, Specifically Dietary Quercetin, Is Associated With Lower Odds Of Frailty Onset Over 12-Years Of Follow-Up Among Adults In The Framingham Heart Study.” This is one of the first community-based studies that comprehensively examined the role of dietary flavonoids for frailty prevention.
more recommended stories
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.
 Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature Identified
Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Microbial Signature IdentifiedKey Points at a Glance NYU.
 Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV Tumors
Nanovaccine Design Boosts Immune Attack on HPV TumorsKey Highlights Reconfiguring peptide orientation significantly.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for Neuroprotection
Acute Ischemic Stroke: New Evidence for NeuroprotectionKey Highlights A Phase III clinical.
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.
 Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?
Can Too Many Antioxidants Harm Future Offspring?Key Takeaways High-dose antioxidant supplementation in.
 Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social Media
Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social MediaKey Summary Anxiety commonly begins in.
 Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in Cancer
Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in CancerKey Takeaways Johns Hopkins researchers developed.

Leave a Comment