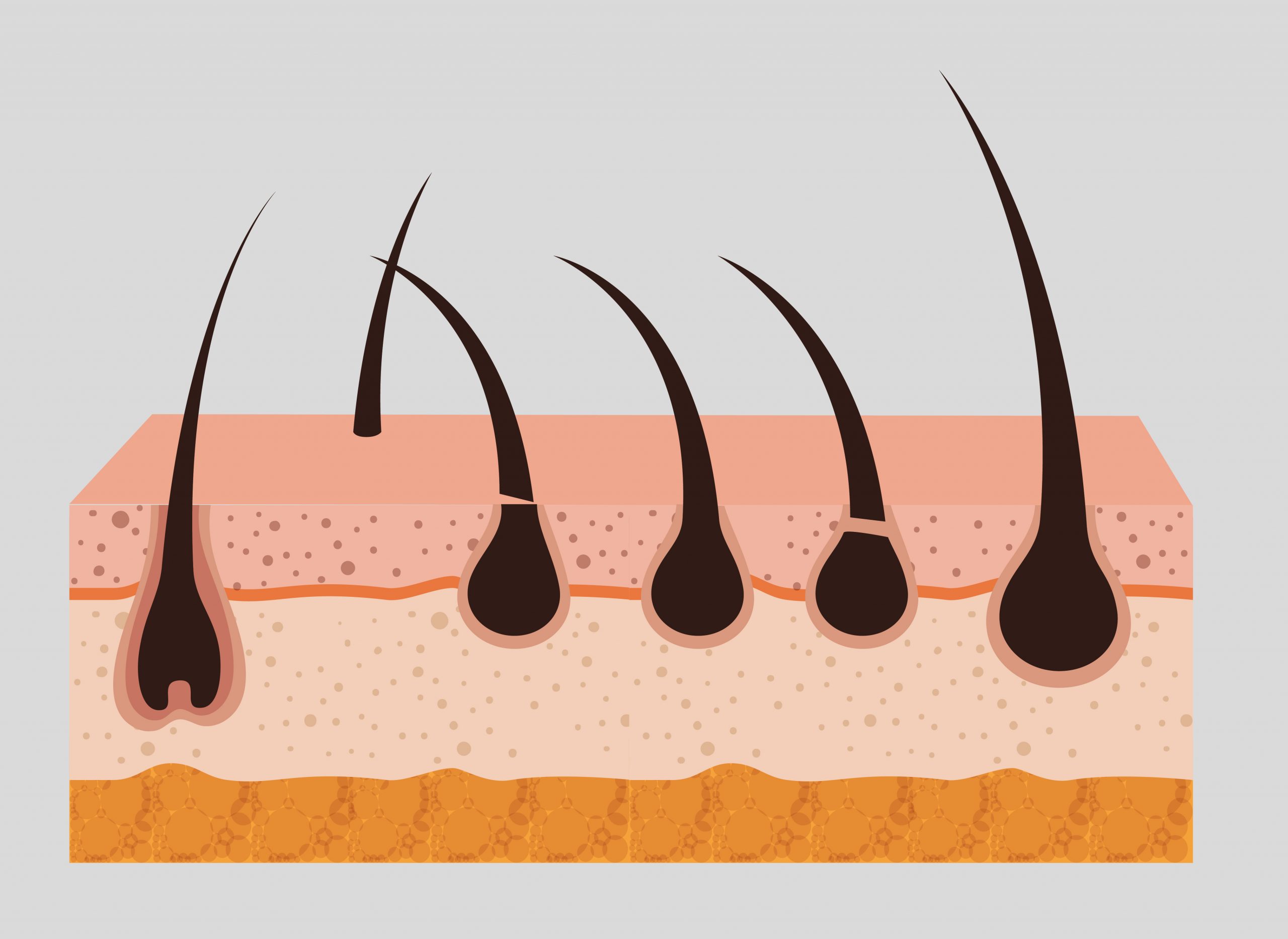

Just as people’s joints stiffen with age, making it difficult to move about, hair follicle stem cells stiffen, making it difficult to develop hair, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study. The scientists discovered that softening MicroRNA cells of the hair follicle increases their likelihood of producing hair.
Northwestern researchers discovered how to soften those stem cells, allowing them to regrow hair. The researchers describe in a mouse study published this week in PNAS that they can soften the stem cells by increasing the synthesis of a little RNA called miR-205, which relaxes the hardness of the cells. Researchers genetically modified stem cells to create more miR-205, which stimulated hair growth in both young and old mice.
“They started to grow hair in 10 days,” said corresponding author Rui Yi, the Paul E. Steiner Research Professor of Pathology and professor of dermatology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. “These are not new stem cells being generated. We are stimulating the existing stem cells to grow hair. A lot of times we still have stem cells, but they may not be able to generate the hair.
“Our study demonstrates the possibility of stimulating hair growth by regulating cell mechanics. Because of the potential to deliver microRNA by nanoparticles directly into the skin, next we will test whether topically delivered miR-205 can stimulate hair growth first in mice. If successful, we will design experiments to test whether this microRNA can promote hair growth potentially in humans.”
This research was carried out in genetically modified mice models. The scientists used advanced microscopy technologies, such as atomic force microscopy and two-photon microscopy, to detect stiffness and track cell activities in live animals.
Jingjing Wang, Yuheng Fu, and Kathleen Green are among the other Northwestern authors.
The article is titled “MicroRNA-205 promotes hair regeneration by modulating mechanical properties of hair follicle stem cells.”
more recommended stories
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US States
Influenza Vulnerability Index Maps Flu Risk Across US StatesKey Points Researchers developed a new.
 Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic Type
Post Amputation Pain Patterns Differ by Prosthetic TypeKey Summary A new study from.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.

Leave a Comment