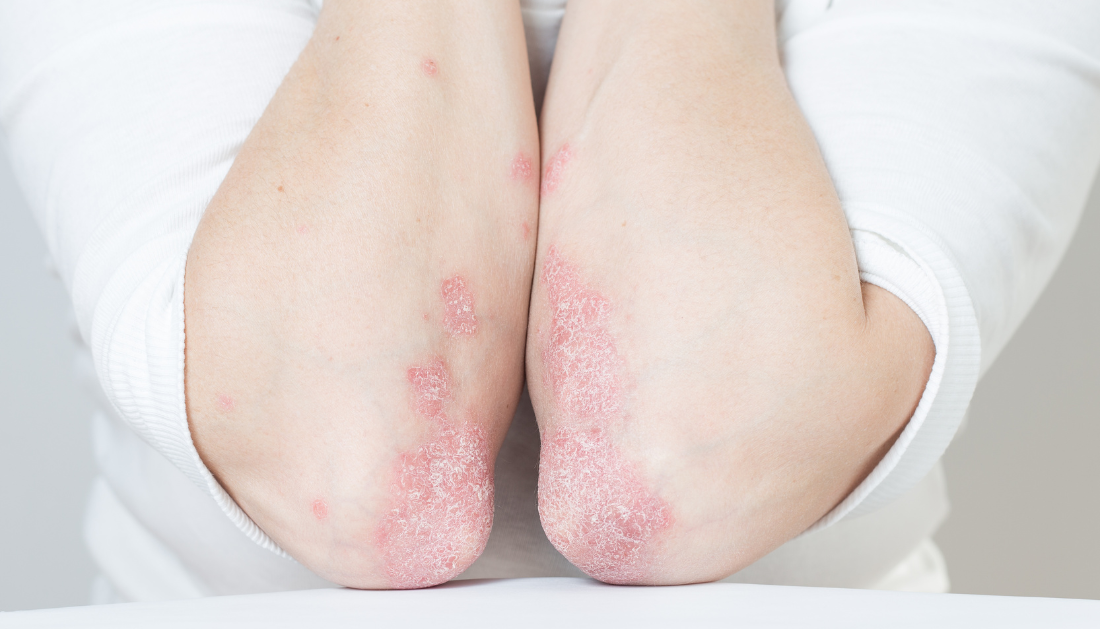

Breakthrough research has discovered new methods for removing immune cells that cause skin autoimmune illnesses while leaving protective cells alone to fight infection and cancer.
The researchers, led by Professor Laura Mackay of the University of Melbourne, a Laboratory Head and Immunology Theme Leader at the Peter Doherty Institute of Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), discovered distinct mechanisms controlling different types of immune cells and discovered that by precisely targeting these mechanisms, they could selectively eliminate ‘problematic cells’ and reshape the skin’s immune landscape.
Our skin is densely packed with specialized immune cells that fight infections and cancer while also promoting healing. These cells, known as tissue-resident T cells or TRM cells, remain in the skin to fight infections and malignant cells. However, if not well managed, some of these skin TRM cells might lead to autoimmune disorders including psoriasis and vitiligo.
Dr. Simone Park of the University of Melbourne, an Honorary Research Fellow and former Postdoctoral Fellow in the Mackay Lab at the Doherty Institute, and the study’s lead first author, stated that this study is the first to describe the unique elements that control various types of skin TRM cells in animal models, providing precise targets for potential treatment strategies.
“Specialized immune cells in our skin are diverse: many are critical to prevent infection and cancer, but others play a big role in mediating autoimmunity,” Dr. Park added.
“We discovered key differences in how distinct types of skin T cells are regulated, allowing us to precisely edit the skin’s immune landscape in a targeted way.”
Dr. Susan Christo of the University of Melbourne, Senior Research Officer in the Mackay Lab at the Doherty Institute and co-first author of the study, described how these findings could boost attempts to cure skin illness.
Most autoimmune therapies treat symptoms rather than the underlying cause.” Conventional treatments for skin problems frequently affect all immune cells indiscriminately, which means we may be wiping out our protective T cells as well,” Dr. Christo explained.
“We didn’t know how to separate ‘bad’ T cells in the skin from ‘good’ protective ones until now.” We found novel chemicals that allow us to specifically eradicate disease-causing T cells in the skin as a result of this research.”
The research team used this new information in a paper published in Science to delete ‘problematic’ cells that can cause autoimmune illnesses while maintaining the ‘good’ cells that are required to sustain protective immunity.
Professor Laura Mackay of the University of Melbourne, the study’s principal author, indicated that the discoveries could pave the door for more accurate and long-lasting therapy for skin illness.
Long-term treatment of skin conditions such as psoriasis and vitiligo is difficult.” Because the T cells that cause disease are difficult to eradicate, patients frequently require lifelong treatment. “Our approach has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat these skin disorders, significantly improving outcomes for people with difficult skin conditions,” Professor Mackay said.
Following the effective ablation of particular cutaneous T cells in animal models, more research is needed to evaluate the efficiency of these techniques in human participants. Dr. Park thinks that the study will spur the development of new skin disease treatments.
“These discoveries bring us one step closer to developing new drugs that durably prevent autoimmune skin disorders without compromising immune protection,” Dr. Park said in a statement.
more recommended stories
 T-bet and the Genetic Control of Memory B Cell Differentiation
T-bet and the Genetic Control of Memory B Cell DifferentiationIn a major advancement in immunology,.
 Ultra-Processed Foods May Harm Brain Health in Children
Ultra-Processed Foods May Harm Brain Health in ChildrenUltra-Processed Foods Linked to Cognitive and.
 Parkinson’s Disease Care Advances with Weekly Injectable
Parkinson’s Disease Care Advances with Weekly InjectableA new weekly injectable formulation of.
 Brain’s Biological Age Emerges as Key Health Risk Indicator
Brain’s Biological Age Emerges as Key Health Risk IndicatorClinical Significance of Brain Age in.
 Children’s Health in the United States is Declining!
Children’s Health in the United States is Declining!Summary: A comprehensive analysis of U.S..
 Autoimmune Disorders: ADA2 as a Therapeutic Target
Autoimmune Disorders: ADA2 as a Therapeutic TargetAdenosine deaminase 2 (ADA2) has emerged.
 Is Prediabetes Reversible through Exercise?
Is Prediabetes Reversible through Exercise?150 Minutes of Weekly Exercise May.
 New Blood Cancer Model Unveils Drug Resistance
New Blood Cancer Model Unveils Drug ResistanceNew Lab Model Reveals Gene Mutation.
 Healthy Habits Slash Diverticulitis Risk in Half: Clinical Insights
Healthy Habits Slash Diverticulitis Risk in Half: Clinical InsightsHealthy Habits Slash Diverticulitis Risk in.
 Caffeine and SIDS: A New Prevention Theory
Caffeine and SIDS: A New Prevention TheoryFor the first time in decades,.

Leave a Comment