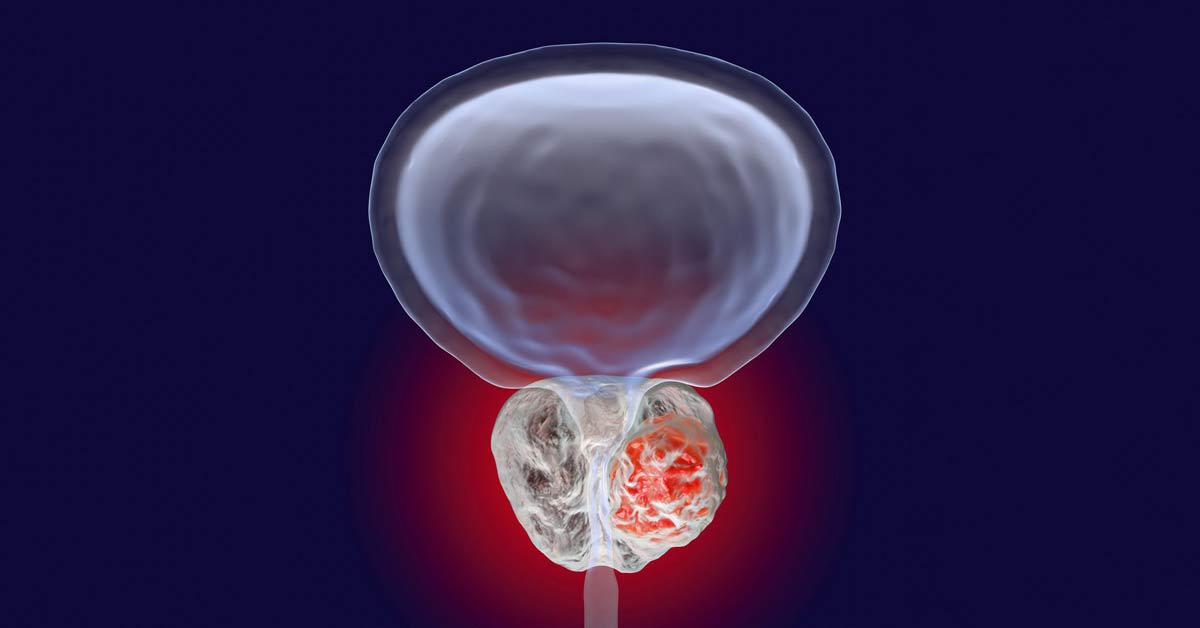

Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in American men. One in eight men will be diagnosed with it during his lifetime according to the American Cancer Society.
Warning Signs of Prostate Cancer
Most cases of prostate cancer don’t have any symptoms. Following the screening guidelines is your best chance of discovering prostate cancer. When it is not discovered early, changes in urination can be the first thing that men notice. Though urinary changes can result from the aging process, they may indicate that something is wrong.
The warning signs of prostate cancer include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Pain or burning during ejaculation
- Frequent urination
- Waking at night to use the bathroom
- Difficulty starting urination
- Difficulty stopping urination
- Flow of urine that’s slower than normal
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Blood in the semen
As cancer progresses, symptoms may include pain in back or spine that is unexplained or weight loss that is unexplained.
Screening
Prostate cancer is a serious disease, but most men diagnosed don’t die from it. More than three million American men who have been diagnosed with the disease are still alive today.
The best way to survive prostate cancer is through early detection. The best chance of early detection is through regular screening, starting at age 40. After your initial screening, your urologist will be able to tell you when to have your next one.
There are two parts of screening. The first part is a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. During the PSA test, blood is drawn from the arm. It is analyzed in a lab for PSA levels. Elevated PSA levels may indicate cancer. They can also be caused by other conditions like an enlarged prostate (BPH) or a urinary tract infection (UTI).
The second part of screening is a digital rectal exam (DRE). During a DRE, the prostate is checked. A urologist inserts a gloved finger into the rectum. They feel the back wall of the prostate gland. The urologist is checking for enlargement, tenderness, lumps, or hard spots that may indicate cancer.
Both parts of the cancer screening are important. Together, they give your urologist valuable information that provides a more complete picture of your health.
Are you experiencing the symptoms of prostate cancer? Are you 40 years old or older and ready for your first or next screening? Schedule your appointment right away!
more recommended stories
 Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent Allergies
Food Tolerance Mechanism: How T Cells Prevent AllergiesKey Summary Researchers at Stanford University.
 Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis Delays
Endometriosis Screening Tool May Cut Diagnosis DelaysKey Points Researchers from the University.
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights Benefits
Dance for Healthy Aging: Study Highlights BenefitsKey Points at a Glance A.
 Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat Diet
Breast Cancer Prognosis Linked to High-Fat DietKey Points A high-fat diet accelerated.
 Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA Analysis
Advanced Prostate Cancer and Serial ctDNA AnalysisKey Takeaways Serial liquid biopsies using.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain Changes
Vascular Health Linked to Early Alzheimer’s Brain ChangesKey Takeaways Brain vascular health is.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.

Leave a Comment