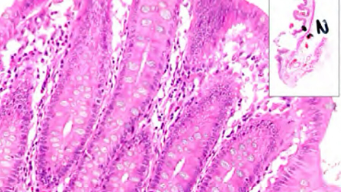

The research addresses the long-recognized poor prognosis of relatively undifferentiated cancers, suggesting that selection against differentiation and in favour of uncontrolled growth is a powerful driver of cancer progression. Goblet cells, which provide the mucous surface of the gut, are a crucial focus of this study. When present in colorectal cancers, these cancers are termed mucinous.
Key findings from the study include:
- Nearly 80 CRC-derived cell lines are classified into five categories based on the levels of MUC2 (the main mucous product of goblet cells) and TFF3 (an associated gene product).
- Identification of five distinct patterns of MUC2 and TFF3 expression, which can be easily identified in tumour specimens, allowing for a finer characterisation of CRCs concerning goblet cell differentiation.
- It was discovered that approximately 30% of all CRCs express TFF3 but not MUC2, a previously unrecognised subgroup.
- Highlighting the role of LGR5 in controlling differentiation rather than direct control of cell growth, challenging previous assumptions.
more recommended stories
 Sickle Cell Gene Therapy Access Expands Globally
Sickle Cell Gene Therapy Access Expands GloballyKey Summary Caring Cross and Boston.
 Reducing Alcohol Consumption Could Lower Cancer Deaths
Reducing Alcohol Consumption Could Lower Cancer DeathsKey Takeaways (At a Glance) Long-term.
 NeuroBridge AI Tool for Autism Communication Training
NeuroBridge AI Tool for Autism Communication TrainingKey Takeaways Tufts researchers developed NeuroBridge,.
 Population Genomic Screening for Early Disease Risk
Population Genomic Screening for Early Disease RiskKey Takeaways at a Glance Population.
 Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood Metabolites
Type 2 Diabetes Risk Identified by Blood MetabolitesKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) Researchers identified.
 Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge Drinking
Microglia Neuroinflammation in Binge DrinkingKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Precision Oncology with Personalized Cancer Drug Therapy
Precision Oncology with Personalized Cancer Drug TherapyKey Takeaways UC San Diego’s I-PREDICT.
 Iron Deficiency vs Iron Overload in Parkinson’s Disease
Iron Deficiency vs Iron Overload in Parkinson’s DiseaseKey Takeaways (Quick Summary for HCPs).
 Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis Insights
Can Ketogenic Diets Help PCOS? Meta-Analysis InsightsKey Takeaways (Quick Summary) A Clinical.
 Silica Nanomatrix Boosts Dendritic Cell Cancer Therapy
Silica Nanomatrix Boosts Dendritic Cell Cancer TherapyKey Points Summary Researchers developed a.

Leave a Comment