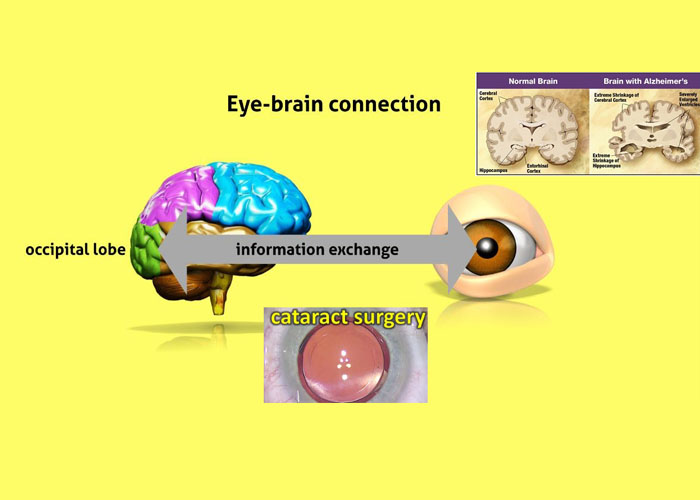

People with newly diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease less likely to have cataract surgery than unaffected people.
The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has increased globally during the last decades. It is well known that suboptimal care of comorbidities can accelerate the course of cognitive decline in AD.
One of these comorbidities, poor vision, is associated with cognitive decline. The most common cause of poor vision and vision loss is cataract, where the opacity of the crystalline lens of the eye is lost. The only Alzheimer’s Disease treatment is rather mini-invasive surgery.
People with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are less likely to have cataract surgery than people without Alzheimer’s disease. The procedure rate starts to decrease already one year after the diagnosis, according to a new study from the University of Eastern Finland.
The lower likelihood of cataract surgery among people with cognitive disorders has been reported previously. This study is the first to report an association between the AD diagnosis and a lower incidence of cataract surgery, and a decrease in the procedure rate related to the time since the diagnosis.
The decrease in the incidence of cataract surgery among people with newly diagnosed AD is concerning because the benefits of this low-risk procedure would probably be similar for people with and without AD.
“The results of the study indicate that people with AD might have a higher threshold for cataract procedures. However, persons with cognitive disorders should be actively referred to ophthalmologic consultations because cataract surgery can improve their cognitive and physical functioning. The stigma of the disease should not lead to fewer referrals to cataract surgery,” the authors say.
The study was conducted as part of the Medication Use and Alzheimer’s Disease Study (MEDALZ), in a cohort which includes 70,718 Finnish community dwellers with AD diagnosed between years 2005 and 2011. They were compared to persons of the same age and gender without AD.
more recommended stories
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NC
Rising Measles Cases Prompt Vaccination Push in NCKey Highlights 15 confirmed Measles cases.
 High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic Health
High-Fat Diets Cause Damage to Metabolic HealthKey Points Takeaways High-fat and ketogenic.
 Chronic Brain Compression Triggers Neuron Death Pathways
Chronic Brain Compression Triggers Neuron Death PathwaysKey Takeaways Chronic brain compression directly.
 Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for Physicians
Texas Medical Board Releases Abortion Training for PhysiciansKey Takeaways Texas Medical Board has.
 Needle-Thin Brain Implant for Layer-Specific Brain Research
Needle-Thin Brain Implant for Layer-Specific Brain ResearchKey Takeaways Researchers have developed a.
 Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy Success
Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy SuccessKey Summary Spanish researchers report complete.
 Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life Experience
Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life ExperienceKey Takeaway Summary Immune cell responses.
 Chronic Pain Linked to CGIC Brain Circuit, Study Finds
Chronic Pain Linked to CGIC Brain Circuit, Study FindsKey Takeaways University of Colorado Boulder.
 High-Intensity Training and Oxidative Stress Insights
High-Intensity Training and Oxidative Stress InsightsNew Evidence Linking High-Intensity Training and.

Leave a Comment