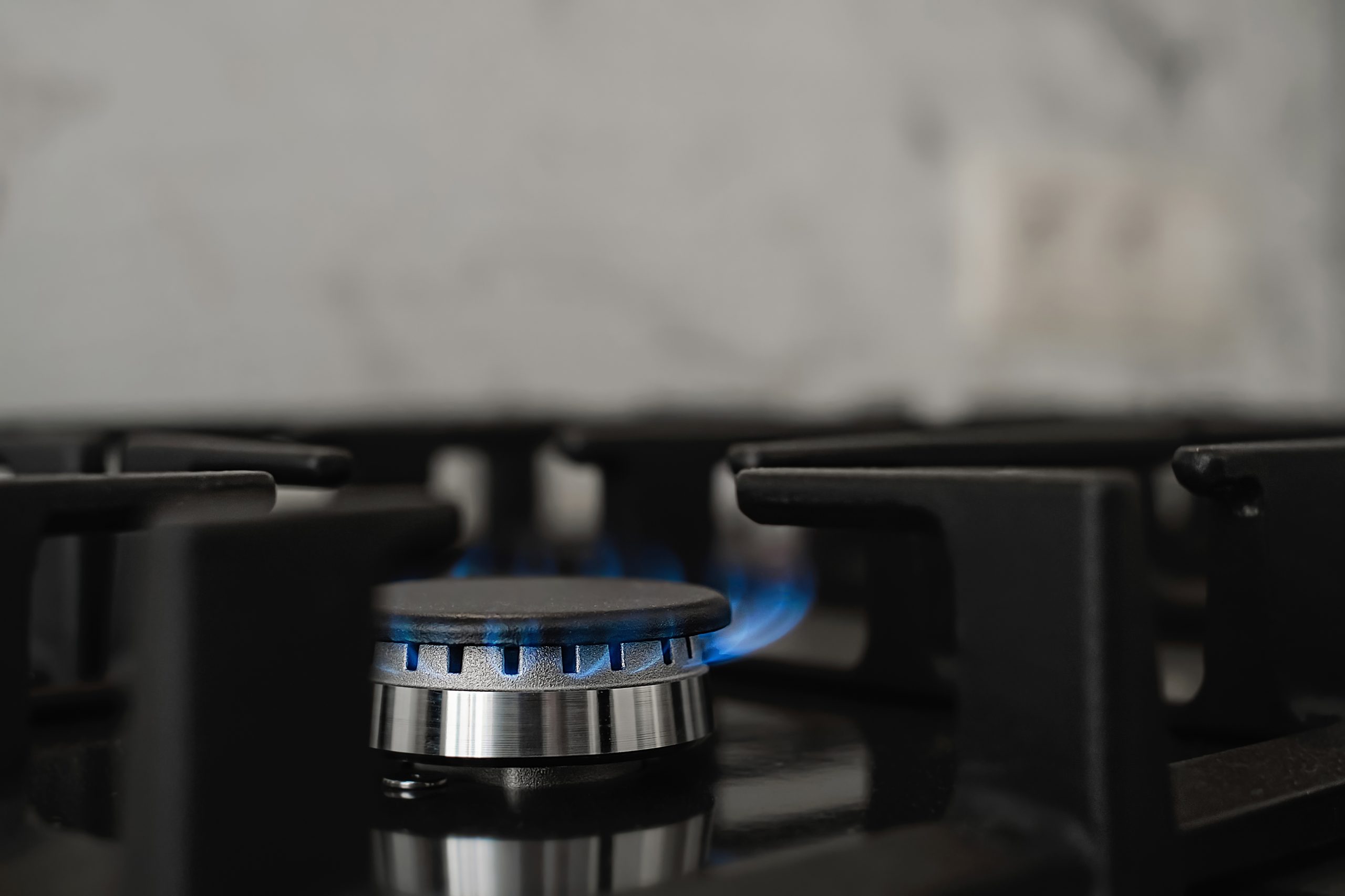


When people fire their gas stoves, a chemical related to an increased risk of leukemia and other blood cell cancers enters their homes. According to a new Stanford-led study, a single gas stovetop burner on high or a gas oven set to 350 degrees Fahrenheit can boost indoor benzene levels above those found in secondhand tobacco smoke. According to the article published in Environmental Science & Technology, benzene also floats throughout a home and remains in the air for hours.
“Benzene forms in flames and other high-temperature environments, such as the flares found in oil fields and refineries. We now know that benzene also forms in the flames of gas stoves in our homes,” said study senior author Rob Jackson, the Michelle and Kevin Douglas Provostial Professor and professor of Earth system science at the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability. “Good ventilation helps reduce pollutant concentrations, but we found that exhaust fans were often ineffective at eliminating benzene exposure.”
Worse than cigarette smoke
Overall, the researchers discovered that indoor benzene concentrations formed in the flames of gas stoves can be worse than average secondhand smoke concentrations, that benzene can migrate into other rooms far from the kitchen, and that concentrations measured in bedrooms can exceed national and international health benchmarks. They also discovered that even when vented outside, domestic range hoods are not always successful at reducing benzene and other pollutants.
The current study is the first to look at benzene emissions when using a stove or oven. Previous research concentrated on leakage from stoves when they were turned off and did not directly evaluate the ensuing benzene amounts. Gas and propane burners and ovens released 10 to 50 times more benzene than electric stoves, according to the researchers. Exposure to benzene increases the risk of blood cell cancer.
Induction cooktops produced no detectable benzene and help lowering the risk of blood cell cancer. The rates of benzene emitted during combustion were hundreds of times higher than rates of benzene emitted from unburned gas escaping into homes observed in other recent investigations.
The researchers also investigated whether cooked meals generate benzene and discovered that pan-frying fish or bacon produced no benzene emissions. The scientists found that the sole cause of benzene emissions was the fuel utilized, not any food prepared.
A recent Stanford-led study found that gas-burning stoves in American households emit methane, which has a climatic impact similar to the carbon dioxide emissions from around 500,000 gasoline-powered cars. Users are also exposed to contaminants such as nitrogen dioxide, which can cause respiratory problems.
A 2013 meta-analysis revealed that children living in houses with gas stoves had a 42% higher risk of asthma than children living in homes without gas stoves, while a 2022 research projected that gas stoves are responsible for 12.7% of juvenile asthma in the United States.
“I’m renting an apartment that happens to have an electric stove,” said study lead Yannai Kashtan, a graduate student in Earth system science. “Before starting this research, I never thought about it twice, but the more we learn about pollution from gas stoves, the more relieved I am to be living without a gas stove.”
How to Reduce Pollutant Exposure from Gas Stoves
Aside from ensuring sufficient ventilation via a range hood or an open window, other relatively low-cost techniques to minimizing pollution from gas stoves include:
- Use portable induction cooktops, which may be purchased new for less than $50.
- Tea kettles, toaster ovens, and slow cookers are examples of electric cookware.
- To offset the expense of upgrading gas appliances, take advantage of state and municipal subsidies as well as low- or no-interest financing (such as these programs for California and the San Francisco Bay Area).
- To assist reduce the expense of replacing gas appliances, federal tax credits are currently available, and federal rebates should be available later this year or perhaps in 2024.
more recommended stories
 Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials Show
Statins Rarely Cause Side Effects, Large Trials ShowKey Points at a Glance Large.
 Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social Media
Anxiety Reduction and Emotional Support on Social MediaKey Summary Anxiety commonly begins in.
 Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in Cancer
Liquid Biopsy Measures Epigenetic Instability in CancerKey Takeaways Johns Hopkins researchers developed.
 Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an Upgrade
Human Antibody Drug Response Prediction Gets an UpgradeKey Takeaways A new humanized antibody.
 Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy Success
Pancreatic Cancer Research: Triple-Drug Therapy SuccessKey Summary Spanish researchers report complete.
 Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life Experience
Immune Cell Epigenome Links Genetics and Life ExperienceKey Takeaway Summary Immune cell responses.
 Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New Study
Dietary Melatonin Linked to Depression Risk: New StudyKey Summary Cross-sectional analysis of 8,320.
 Chronic Pain Linked to CGIC Brain Circuit, Study Finds
Chronic Pain Linked to CGIC Brain Circuit, Study FindsKey Takeaways University of Colorado Boulder.
 New Insights Into Immune-Driven Heart Failure Progression
New Insights Into Immune-Driven Heart Failure ProgressionKey Highlights (Quick Summary) Progressive Heart.
 Microplastic Exposure and Parkinson’s Disease Risk
Microplastic Exposure and Parkinson’s Disease RiskKey Takeaways Microplastics and nanoplastics (MPs/NPs).

Leave a Comment