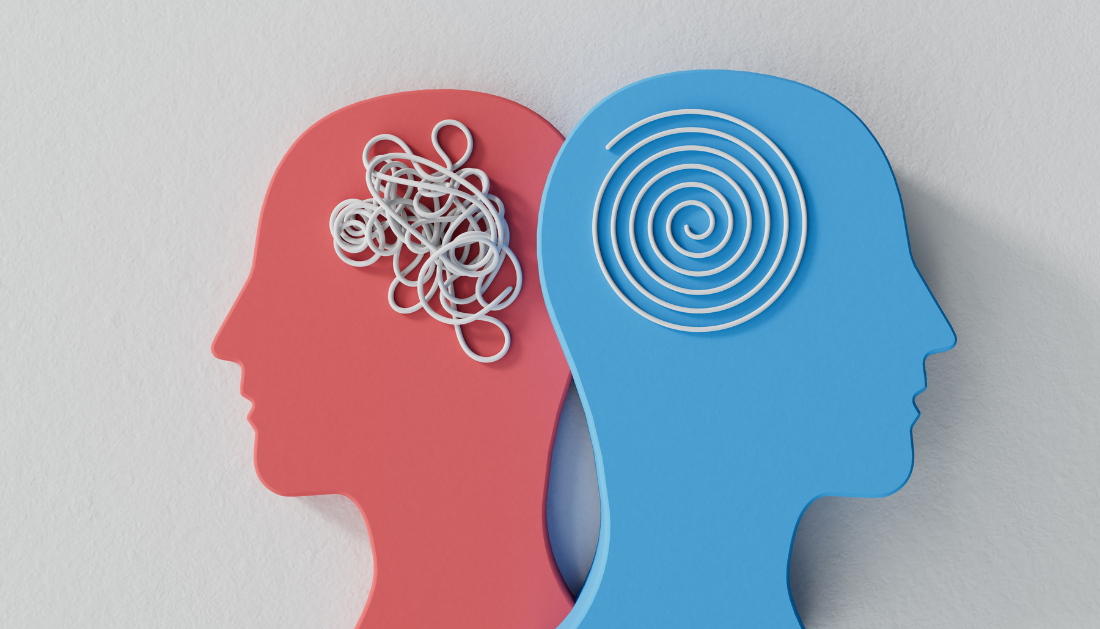


In a recent publication featured in the esteemed journal Nature Reviews Psychology, scholars deliberated upon the intricacies of personality change, delineating four fundamental facets — preconditions, triggers, reinforcers, and integrators — orchestrating effective alterations in personality. Concurrently, they dissected the counterbalancing forces thwarting enduring shifts in personality by fostering stability.
Background Personality encompasses the spectrum of emotional responses, behavioral patterns, aspirations, and cognitive faculties influenced by individual disparities in life aspirations, self-regard, principles, contentment, and assorted traits. The capacity to modulate specific dimensions of one’s personality proves indispensable to outcomes in various spheres of life, encompassing social dynamics, professional achievements, life expectancy, and affluence. Recent longitudinal inquiries have underscored the malleability of personalities across an individual’s lifespan, indicating that while they may exhibit stability over protracted periods, personalities seldom ossify.
Moreover, the pliability of personality and its prognostic efficacy in the long run have galvanized substantial scholarly interest in elucidating the determinants of personality shifts and implementing deliberate interventions. However, extant studies have predominantly scrutinized the impact of overarching macroscopic processes, such as significant life events, in precipitating personality changes. The mechanisms underpinning personality modifications through intervention studies largely elude scrutiny.
About the Study
In this comprehensive review, researchers scrutinized the underlying mechanisms and modalities facilitating personality metamorphosis. Embarking on a holistic exploration of personality dynamics, they partitioned the temporal trajectory of change into four components encapsulating diverse constructs, diverging from a narrow focus on a singular facet of the process.
While acknowledging the contributory role of biological and genetic mechanisms to personality alterations, this review accentuates environmental determinants catalyzing shifts in personality. Additionally, it delves into the factors curbing potential personality alterations by fortifying stability. Empirical findings from investigations into interventions and life events were also examined to glean insights into the mechanisms driving personality change.
Mechanisms
The mechanisms underpinning personality metamorphosis can broadly be classified into three strata: those effectuating direct alterations, time- or context-specific modifications, and ingrained habits contingent upon particular environments. These strata are intricately interconnected, with perturbations at one level often reverberating across other levels.
Personality development theories posit that the processes and mechanisms engendering personality change vary in depth and scope. To dissect these mechanisms, researchers delineated four pivotal categories — preconditions, triggers, reinforcers, and integrators — pivotal in precipitating change.
The circumstances conducive to change are termed preconditions. Deliberate alterations to one’s character necessitate the impetus or aspiration for transformation, either for the attainment of other objectives or as an end in itself. The scholars posit that enduring and profound shifts in personality are unattainable unless individuals actively pursue the changes they seek. Occasionally, environmental factors beyond an individual’s control, such as injury or incarceration, may precipitate personality change, constituting preconditions as well.
Experiences instigating modifications in behavior, transient emotional states, aspirations, or mental processes are labeled triggers, encompassing internal elements like stress or physiological reactions, and external factors such as specific contexts or occurrences. Therapeutic interventions, life-altering events, emotion regulation strategies, and social obligations serve as environmental triggers catalyzing alterations at the level of transient states. Through concrete illustrations, the researchers scrutinized the direct interplay between triggers and transient manifestations in an individual.
Sustained alterations in transient states are imperative for enduring changes in personality. Internal and external reinforcements serve to perpetuate the triggers inducing shifts in behavior, aspirations, mental processes, and transient emotional states, thereby facilitating enduring personality transformations. The scholars exemplify this phenomenon by citing the rewarding effect of a substantial salary on diligent conduct within a productive work environment.
However, the perpetuation of reinforced personality change hinges upon the conversion of habits into enduring changes at the level of traits. This necessitates the integration of novel behaviors, aspirations, emotional responses, and cognitive patterns from one facet of an individual’s life into other domains. The review advocates for introspection as a means of assimilating changes in behavior, emotional responses, cognitive processes, or aspirations into one’s character.
Stabilizing Mechanisms
The review also deliberates on mechanisms fostering stability and curtailing changes. Personality alterations are constrained by the inclination to maintain familiarity or a consistent identity. Inadequacies in reinforcing alterations, insufficient triggers, attributing changes to external factors, among other mechanisms, serve to bolster stability and impede change.
Conclusions
In sum, the review offers an exhaustive exploration of the mechanisms underpinning personality shifts, whether deliberate or induced by environmental factors such as life-altering events. Through concrete illustrations, the researchers elucidate how these mechanisms present potential avenues for effecting enduring personality modifications. Nevertheless, they contend that personality changes typically manifest modestly and rarely in a drastic manner, even within the context of interventions.
For more information: The Process and Mechanisms of Personality Change, Nature Reviews Psychology, https://doi.org/10.1177/08902070231190219
more recommended stories
 Brain Pulsations Linked to High BMI
Brain Pulsations Linked to High BMIAccording to a new study from.
 Brain Age Estimation: EEG Advancements in Neurology
Brain Age Estimation: EEG Advancements in NeurologyTo estimate brain age using EEG.
 Unlocking Ketogenic Diet for Epilepsy Management
Unlocking Ketogenic Diet for Epilepsy ManagementExploring the Therapeutic Potential of Ketogenic.
 Senescence in Neurons: Findings
Senescence in Neurons: FindingsBased on a new study by.
 Balanced Diet Linked to Enhanced Brain Health
Balanced Diet Linked to Enhanced Brain HealthDiet and brain health are strongly.
 Acid-Reducing Drugs Linked to Higher Migraine Risk
Acid-Reducing Drugs Linked to Higher Migraine RiskIndividuals who utilize acid-reducing drugs may.
 Atrial Fibrillation in Young Adults: Increased Heart Failure and Stroke Risk
Atrial Fibrillation in Young Adults: Increased Heart Failure and Stroke RiskIn a recent study published in.
 Neurodegeneration Linked to Fibrin in Brain Injury
Neurodegeneration Linked to Fibrin in Brain InjuryThe health results for the approximately.
 DELiVR: Advancing Brain Cell Mapping with AI and VR
DELiVR: Advancing Brain Cell Mapping with AI and VRDELiVR is a novel AI-based method.
 Retinal Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s Disease
Retinal Neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s DiseaseBy measuring the thickness of the.

Leave a Comment