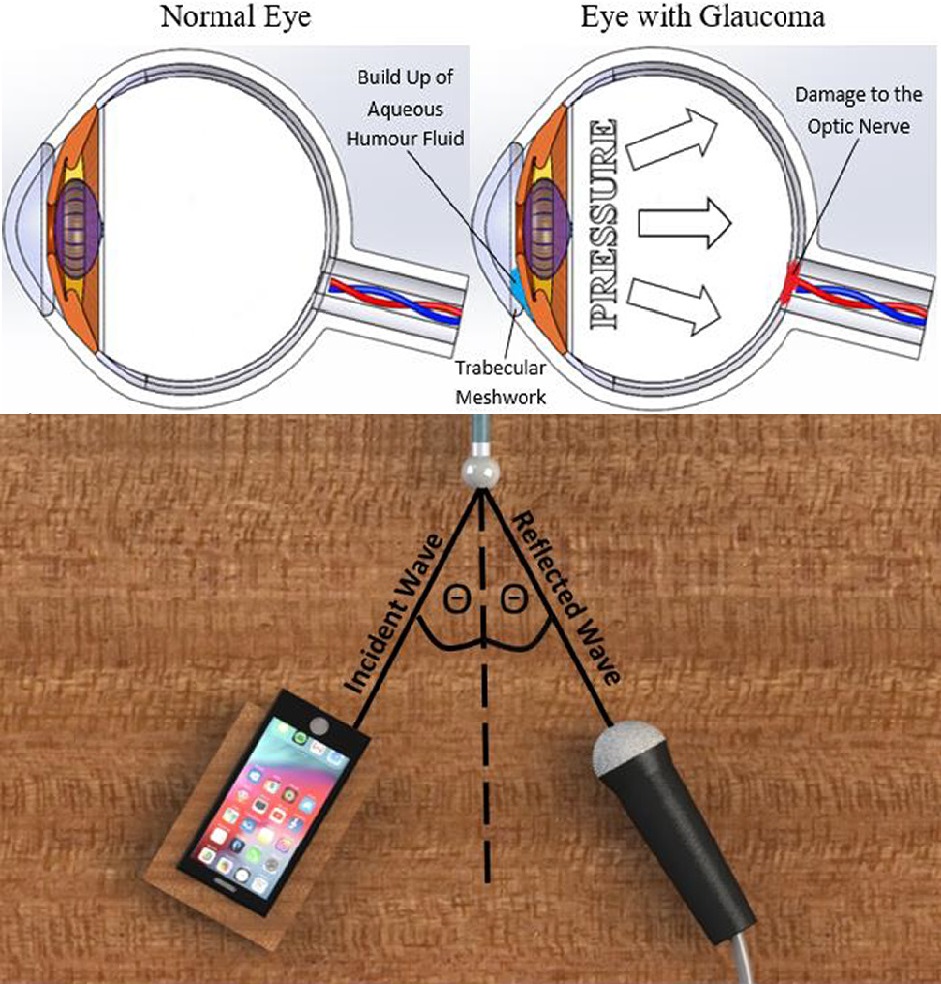

The human eye is a very sensitive and cherished organ for its unparalleled use for humans on a daily basis. Thus, its continued state of health is of upmost importance to individuals worldwide. Some of the most common eye related diseases – Glaucoma are often avoidable and display strong risk factors some time before their onset.
For example, in the case of diabetic retinopathy, individuals with diabetes are specifically at risk and so are constantly monitored for background retinopathy, tiny bulges that develop in the blood vessels of the eye.
However, in the case of glaucoma, an ocular disease with age and elevated levels of intraocular pressure (IOP) as significant risk factors, it is harder to specify such a specific group of individuals at risk of development.
For this reason, an accurate, non‐invasive, mobile measurement of IOP would provide a means to continuously monitor an individual’s IOP over an extended period. This would lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of the condition, drastically increasing the chances of maintaining the individual’s vision.
Intraocular pressure (IOP)
Early detection of increasing values of intraocular pressure (IOP) due to glaucoma can prevent severe ocular diseases and ultimately, prevent loss of vision. Currently, the need for an accurate, mobile measurement of IOP that shows no correlation to central corneal thickness is unmet within the modern healthcare practices. There is a potential to utilize soundwaves as a mobile measurement method.
However, according to the study experiment showing comprehensively that there is a relationship between the internal pressure of an object and its acoustic reflection coefficient, providing a confirmation of the theory that would allow mobile measurements of IOP to be conducted with the use of a smart phone.
Smartphones could be used to scan people’s eyes for early-warning signs of glaucoma – helping to prevent severe ocular diseases and blindness, a new study reveals.
Some of the most common eye-related diseases are avoidable and display strong risk factors before onset, but it is much harder to pinpoint a group of people at risk from glaucoma.
Glaucoma is associated with elevated levels of intraocular pressure (IOP) and an accurate, non-invasive way of monitoring an individual’s IOP over an extended period would help to significantly increase their chances of maintaining their vision.
Soundwaves used as a mobile measurement method would detect increasing values of IOP, prompting early diagnosis and treatment.
Scientists have successfully carried out experiments using soundwaves and an eye model, publishing their findings in Engineering Reports.
Co-author Dr. Khamis Essa, Director of the Advanced Manufacturing Group at the University of Birmingham, commented: “We discovered a relationship between the internal pressure of an object and its acoustic reflection coefficient.
With further investigation into eye geometry and how this affects the interaction with soundwaves, it is possible to use a smartphone to accurately measure IOP from the comfort of the user’s home.”
Risk factors for other eye diseases are easier to assess – for example, in the case of diabetic retinopathy, individuals with diabetes are specifically at risk and are constantly monitored for tiny bulges that develop in the blood vessels of the eye.
The current ‘gold standard’ method of measuring IOP is applanation tonometry, where numbing drops followed by non-toxic dye are applied to the patient’s eyes. There are problems and measurement errors associated with this method.
Risk factors of Glaucoma
An independent risk factor of glaucoma is having a thin central corneal thickness (CCT) – either by natural occurrence or a common procedure like laser eye surgery.
A thin CCT causes artificially low readings of IOP when using applanation tonometry. The only way to verify the reading is by a full eye examination – not possible in a mobile situation. Also, the equipment is too expensive for most people to purchase for long-term home monitoring.
IOP is a vital measurement of healthy vision, defined as pressure created by continued renewal of eye fluids. Ocular hypertension is caused by an imbalance in production and drainage of aqueous fluid – most common in older adults. Risk increases with age, in turn increasing the likelihood of an individual developing glaucoma.
Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve which is estimated to affect 79.6 million people world-wide and, if left untreated, causes irreversible damage. In most cases, blindness can be prevented with appropriate control and treatment.
more recommended stories
 Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie Cells
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Combo Therapy Targets Zombie CellsKey Points Researchers from Mayo Clinic.
 Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the Heart
Heart Attack Recovery: Single Injection May Heal the HeartKey Points Researchers have developed a.
 Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver Fibrosis
Fragmentome Technology Detects Early Liver FibrosisKey Points at a Glance AI-based.
 CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin Defects
CTNNB1 Syndrome Study Explores Beta-Catenin DefectsKey Takeaways Researchers in Spain are.
 Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental Antibiotics
Tuberculosis Breakthrough with Experimental AntibioticsKey Takeaways Experimental antibiotics disrupt a.
 National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal Support
National Healthy Longevity Trial Receives Federal SupportKey Summary Up to $38 million.
 Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under Hypoxia
Red Blood Cells Improve Glucose Tolerance Under HypoxiaKey Takeaways for Clinicians Chronic hypoxia.
 Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological Risk
Nanoplastics in Brain Tissue and Neurological RiskKey Takeaways for HCPs Nanoplastics are.
 AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell Transplant
AI Predicts Chronic GVHD Risk After Stem Cell TransplantKey Takeaways A new AI-driven tool,.
 Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes Odds
Red Meat Consumption Linked to Higher Diabetes OddsKey Takeaways Higher intake of total,.

Leave a Comment